Epoch Times, Science – News, Beyond Science, Space, & Mysteries | The Epoch Times https://www.theepochtimes.com The Epoch Times is an independent voice in print and on the web. We report news responsibly and truthfully so that readers can improve their own lives and increase their understanding and respect for their neighbors next door and around the globe. Sat, 14 Dec 2019 18:13:33 +0000 en-US hourly 1 Plants Emit Ultrasonic Screams When Stressed: Study https://www.theepochtimes.com/plants-emit-ultrasonic-screams-when-stressed-study_3170053.html Tue, 10 Dec 2019 14:58:49 +0000 Some plants emit a high frequency distress sound when they are placed under environmental stress, a team of researchers at Tel Aviv University in Israel has found.
The team, led by Itzhak Khait, examined the sounds emitted by tomato and tobacco plants when stressed by insufficient water or when their stems are cut. Microphones recorded ultrasonic sounds between 20 and 100 kilohertz emitted by the plants in both cases, the study found.
The sounds emitted by the stressed plants are at frequencies unable to be heard by humans, however the team of scientists believes “some organisms” can hear the sounds from up to several meters away.
A tomato plant emitted 25 ultrasonic distress sounds in the space of an hour when its stem was cut, according to the study. In contrast, tobacco plants emitted 15 distress sounds when their stems were cut.
When deprived of water, the tomato plants sent out 35 ultrasonic sounds in the course of an hour, while 11 were emitted by the tobacco plants. The team observed that the sounds released when the plants were deprived of water were louder compared to the ones when having their stems cut.
In comparison, plants not placed under any environmental stress emitted less than one distress sound per hour.
The authors noted that other plants and animals—and humans with the correct tools—could hear and listen to the plants silent screams. A moth, for example, may choose to lay its eggs elsewhere if it is able to detect that a plant is water-stressed, according to the study, which has not yet been published in a journal.
In other cases, plants could react accordingly to others which lack water, the authors suggest.
“These findings can alter the way we think about the plant kingdom, which has been considered to be almost silent until now,” the researchers write in their study.

The Tel Aviv University team then took the data and used it to train a machine-learning model to predict the possible frequencies plants could emit while undergoing different forms of environmental stress, such as during intense rain or wind.
The team also believes other plants may release distress sounds when placed under stress.
“More investigation on plant bioacoustics in general and on sound emission in plants in particular may open new avenues for understanding plants and their interactions with the environment, and it may also have a significant impact on agriculture,” the authors suggested.
The notion that “sounds that drought-stressed plants make could be used in precision agriculture seems feasible if it is not too costly to set up the recording in a field situation,” Anne Visscher, a fellow in the Department of Comparative Plant and Fungal Biology at the Royal Botanic Gardens in the UK told New Scientist.
]]> Surprising 1st Results From NASAs Sun-Skimming Spacecraft https://www.theepochtimes.com/surprising-1st-results-from-nasas-sun-skimming-spacecraft_3166134.html Thu, 05 Dec 2019 16:54:25 +0000 CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla.—NASAs sun-skimming spacecraft, the Parker Solar Probe, is surprising scientists with its unprecedented close views of our star.
Scientists released the first results from the mission Wednesday. They observed bursts of energetic particles never seen before on such a small scale as well as switchback-like reversals in the out-flowing solar magnetic field that seem to whip up the solar wind.
NASAs Nicola Fox compared this unexpected switchback phenomenon to the cracking of a whip.
“Theyre striking and its hard to not think that theyre somehow important in the whole problem,” said Stuart Bale of the University of California, Berkeley, who was part of the team.
Researchers said they also finally have evidence of a dust-free zone encircling the sun. Farther out, theres so much dust from vaporizing comets and asteroids that one of 80 small viewfinders on one instrument was pierced by a grain earlier this year.
“I cant say that we dont worry about the spacecraft. I mean, the spacecraft is going through an environment that weve never been before,” Fox said.
Launched in 2018, Parker has come within 15 million miles (25 million kilometers) of the sun and will get increasingly closer—within 4 million miles (6 million kilometers)—over the next six years. Its completed three of 24 orbits of the sun, dipping well into the corona, or upper atmosphere. The goal of the mission is to shed light on some of the mysteries surrounding the sun.


Parker will sweep past Venus on Dec. 26 for the second gravity-assist of the $1.5 billion mission and make its fourth close solar encounter in January.
The findings in the journal Nature were made during a relatively quiet phase of solar activity.
“Were just starting to scratch the surface of this fascinating physics,” said Princeton Universitys David McComas, the chief scientist of one of the spacecrafts instruments.
As Parker gets even closer to its target, the sun will go through an active phase “so we can expect even more exciting results soon,” University College Londons Daniel Verscharen wrote in an accompanying editorial. Verscharen was not part of the mission.

Over the summer, Fox shared these early results with solar astrophysicist Eugene Parker, 92, professor emeritus at the University of Chicago for whom the spacecraft is named. He expressed excitement—“wow”—and was keen to be involved.
Its the first NASA spacecraft to be named after a person still alive. Parker attended its launch last year from Cape Canaveral.
By Marcia Dunn
]]> Yellowstone Area Experiences 193 Earthquakes in a Month: Report https://www.theepochtimes.com/yellowstone-area-experiences-193-earthquakes-in-a-month-report_3155420.html Mon, 25 Nov 2019 12:11:40 +0000 Yellowstone National Park in Wyoming experienced 193 earthquakes in October, according to a report by monitoring services from the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS).
The park is home to the largest and most diverse collection of natural thermal features in the world and spans an area of 3,470 square miles, comprising of lakes, canyons, rivers, mountain ranges and the Yellowstone Caldera–the largest supervolcano on the continent.
According to the USGS, the tremors from the earthquakes were relatively small, with the largest on Oct. 16 registering at magnitude 2.9 and located 16 miles southeast of Mammoth, Wyoming.
A swarm of 39 earthquakes also hit the west area of Yellowstone on between Oct. 4 to 12, while 87 more occurred between Oct. 26 to 31.
However, sequences like these are “common and account for roughly roughly 50 percent of the total seismicity in the Yellowstone region,” according to the report.
According to Earth Sky, three enormous eruptions occurred at the Yellowstone hotspot 2.1 million, 1.3 million, and 640,000 years ago. However it is unlikely that another super volcanic eruption will occur in the next few thousand years.


Yellowstone is being continuously monitored for signs for an eruption, such as earthquake swarms that indicate magma is moving beneath the surface. The data is regularly updated and published on the U.S. Geological Survey website and scientists believe that they would be able to detect any signs of an impending eruption at least a few weeks before it happens.
Earlier this year in March, USGS addressed reports that Yellowstone was “overdue” for eruption following reports that it would explode at any moment, sparking concern.


Michael Poland, Scientist-in-Charge of the Yellowstone Volcano Observatory, wrote: “In a word, no. In two words, no way. In three words, not even close. Yellowstone doesnt work that way.
“In terms of large explosions, Yellowstone has experienced three—at 2.08, 1.3, and 0.631 million years ago. This comes out to an average of about 725,000 years between eruptions. That being the case, we still have about 100,000 years to go, but this number is based on very little data and so is basically meaningless (would you base any conclusion on the average of just two numbers?).”
Poland further stressed that Yellowstone would not be erupting anytime soon burying Wyoming, Utah, and Colorado in several feet of toxic volcanic ash.
“No matter how you slice it, Yellowstone is not overdue. No. No way. Not even close. But we cant say the same about the oil change for your car, so you might want to check on that,” Poland concluded.
]]> NASA Finds Sugar Molecules Essential to Life in Meteorites That Crashed to Earth https://www.theepochtimes.com/nasa-finds-sugar-molecules-essential-to-life-in-meteorites-that-crashed-to-earth_3156124.html Mon, 25 Nov 2019 07:22:00 +0000 An international team of scientists at NASA have found sugar molecules on two different meteorites, the agency announced on Nov. 19.
The new discovery adds to the growing list of biologically important compounds that have been found in meteorites and supports the theory that chemical reactions in asteroids can play an important role in creating and supporting life, the space agency said in a statement.
Researchers said they discovered “ribose and other bio-essential sugars” in the extraterrestrial rock, adding that ribose is a “crucial component of RNA (ribonucleic acid)”—essential for the regulation and expression of genes.
“In much of modern life, RNA serves as a messenger molecule, copying genetic instructions from the DNA molecule (deoxyribonucleic acid) and delivering them to molecular factories within the cell called ribosomes that read the RNA to build specific proteins needed to carry out life processes,” they explained.
In a study published Monday in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, researchers analysed three separate meteorites, including one dating back billions of years that landed in Australia in 1969.
Previous attempts were made to investigate the meteors for sugar. However this time, the researchers decided to utilize a new technique using hydrochloric acid and water, and found sugars like arabinose and xylose in addition to the significant find of ribose.
“Other important building blocks of life have been found in meteorites previously, including amino acids (components of proteins) and nucleobases (components of DNA and RNA), but sugars have been a missing piece among the major building blocks of life,” the studys lead author, Yoshihiro Furukawa, said in a statement.
The discovery of ribose also suggests that RNA evolved first and was later replaced by DNA because RNA molecules have capabilities that DNA lack, adding to the evidence that scientists are using to develop a clearer understanding of how life may have formed.
“RNA can make copies of itself without help from other molecules, and it can also initiate or speed up chemical reactions as a catalyst. The new work gives some evidence to support the possibility that RNA coordinated the machinery of life before DNA,” the report said.
Furukawa added: “The research provides the first direct evidence of ribose in space and the delivery of the sugar to Earth. The extra-terrestrial sugar might have contributed to the formation of RNA on the prebiotic Earth which possibly led to the origin of life.”
The research team now plans to analyze more meteorites to see how abundant these sugars are and if have they a left-handed or right-handed bias, as some molecules come in two varieties which are mirror images of each other.
“On Earth, life uses left-handed amino acids and right-handed sugars. Since its possible that the opposite would work fine–right-handed amino acids and left-handed sugars. Scientists want to know where this preference came from,” the report explained.
In January, a report published by the American Association for the Advancement of Science said that researchers had found that two meteorites held other ingredients for life.
They included amino acids, hydrocarbons, other organic matter, and traces of liquid water which could date back to the earliest days of the solar system.
]]> Experts Analyze US Decision to Withdraw From Paris Climate Accord https://www.theepochtimes.com/experts-analyze-u-s-decision-to-withdraw-from-paris-climate-accord_3143942.html Tue, 12 Nov 2019 06:52:07 +0000 Secretary of State Mike Pompeo announced in a statement on Nov. 4, that the United States will be withdrawing from the Paris climate accord. President Trump first announced his intention to withdraw from the climate proposal back in 2017.
The decision has garnered both support and criticism from various people and organizations. The Epoch Times reached out to The Heartland Institute, a national free-market think tank, to take an in-depth look at the situation.
Anthony Watts, senior research fellow of environment and climate at The Heartland Institute, explained that the Paris climate accord is ineffective in achieving the goal of reducing climate change.
Researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) found that the world will continue to warm over the years. Similar to previous agreements, although initiatives such as the Paris climate accord are “a step in the right direction,” the overall impact is still insufficient.
Referring to the research Watts said that “the net end result in 2100 would be about a two-tenths of a degree centigrade drop in temperatures. And so thats compared to a gain in three-and-a-half degrees if you believe the climate model.”
While some policy is better than nothing, a cost-benefit analysis indicates that the United States would be placed at a competitive disadvantage compared to other countries if it followed through with the Paris climate accord.
Watts explained that even if the Paris climate accord worked, the end result would have been at the expense of large amounts of money, economic development, and jobs.
The agreement would negatively impact the United States economy in the long run.
“According to analysis that weve done here at The Heartland Institute and others, it [Paris Climate Accord] would have cost us about 2.7 million jobs by 2025 due to scaling back parts of industries. Now that would have been about 440,000 manufacturing jobs that we would have lost associated with that [Paris climate accord],” said Watts.
He continued that by 2030, the United States would see a 38 percent decrease in iron and steel production, a 31 percent decrease in natural gas production, and an 86 percent decrease in coal production. The United States would see a loss of 3 trillion dollars worth of gross domestic product (GDP) and 6.5 million jobs lost by 2040 in the industrial sector.
Regarding carbon dioxide, Watts explained that existing data indicates that carbon dioxide emissions in the United States and the European Union have been generally constant or decreasing between 1970 and 2018. This is partly due to switching to natural gas and renewable energy.
Sen. John Barrasso (R-Wyo.) echoed this, saying that “our reduction in emissions was largely from new and innovative technologies from the private sector—not international agreements or punishing regulations.”
Nonbinding Agreement
The main criticism regarding the Paris climate accord is the nonbinding aspect. Despite signing the agreement, countries do not face any repercussions if they do not follow through with taking steps to protect the climate and environment.
According to Article 6 of the agreement, “Parties recognize that some parties choose to pursue voluntary cooperation in the implementation of their nationally determined contributions to allow for higher ambition in their mitigation and adaptation actions and to promote sustainable development and environmental integrity.”
Essentially, the agreement is a set of guidelines that countries have signed, expressing their interest in developing programs aimed at protecting the environment and climate.
Watts described how countries such as China, despite signing the agreement, have not taken concrete steps to reduce the countrys pollution and carbon dioxide output.
He noted that China continues to build coal plants among other facilities that greatly contribute to the countrys rise in carbon dioxide emissions. India sees a similar increase in emissions.
“The bottom line here is that even if the United States continued with the Paris agreement, the impacts we would be getting from the increases from China and India would totally overshadow the gains that the United States may have made in carbon dioxide reductions related to the Paris accord,” explained Watts.
The decision to withdraw from the agreement has been supported by Republican lawmakers, many of whom cosponsored H.Res.676. The resolution encourages the withdrawal from the Paris agreement.
“The Paris agreement penalized the United States economy and its citizens for the sole purpose of chasing an unobtainable goal, which even if met, would result in only a small reduction in global temperature. President Trump was correct to extract us from this boondoggle,” Watts said.
]]> Googles Project Nightingale Secretly Gathers Personal Health Data on Millions of Americans https://www.theepochtimes.com/googles-project-nightingale-secretly-gathers-personal-health-data-on-millions-of-americans_3143843.html Tue, 12 Nov 2019 05:06:54 +0000 Google has been working with one of the largest healthcare systems in the U.S. to collect and analyze the personal health information of millions of citizens across 21 states, The Wall Street Journal reports.
The Tech giant reportedly teamed up with St. Louis-based Ascension, the largest non-profit health system in the country, last year, and the data sharing has accelerated since summer.
Code-named Nightingale, the project saw both companies collect personal data from patients, which included lab results, doctor diagnoses, and hospitalization records, as well as patient names and dates of birth.
Google said it plans to use the data to create new software that will improve patient care and suggest changes to their care.
Patients and doctors were not notified that their data is being shared, and did not give their consent, according to the report.
One individual who was familiar with the project told the Journal that at least 150 Google employees already have access to much of the data on tens of millions of patients.
Just hours after the secret project was revealed, the two companies announced the collaboration in a press release, in which they said the joint project would see Ascensions data moved onto Googles Cloud platform.
The statement said the joint project aims to “optimize the health and wellness of individuals and communities and deliver a comprehensive portfolio of digital capabilities that enhance the experience of Ascension consumers, patients, and clinical providers across the continuum of care.”
Eduardo Conrado, Executive Vice President of Strategy and Innovations at Ascension, said: “As the healthcare environment continues to rapidly evolve, we must transform to better meet the needs and expectations of those we serve as well as our own caregivers and healthcare providers.
“Doing that will require the programmatic integration of new care models delivered through the digital platforms, applications, and services that are part of the everyday experience of those we serve.”
The partnership will also explore artificial intelligence and machine learning applications to help improve clinical quality, and effectiveness, patient safety and increase consumer and provider satisfaction, according to the statement.
Tariq Shaukat, President of Google Cloud, added: “Ascension is a leader at increasing patient access to care across all regions and backgrounds, particularly those in disadvantaged communities. Were proud to partner with them on their digital transformation.
“By working in partnership with leading healthcare systems like Ascension, we hope to transform the delivery of healthcare through the power of the cloud, data analytics, machine learning, and modern productivity tools—ultimately improving outcomes, reducing costs, and saving lives.”
Ascension also said that its work with Google had been compliant with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act 1996 (HIPAA) and “underpinned by a robust data security and protection effort and adherence to Ascensions strict requirements for data handling.”
]]> Youre Still Alive After Death Say Researchers, Whore Studying the Conscious Mind https://www.theepochtimes.com/youre-still-alive-after-death-say-researchers-whore-studying-the-conscious-mind-2_2954766.html Fri, 08 Nov 2019 09:30:59 +0000 What happens after you die? A team of researchers in New York may have come close to solving this mystery. Theyve concluded that one remains fully conscious at the time of death.
Previously, skeptics would brush aside claims of near-death experiences and often ascribe these to physiological and psychological factors. However, in a study, researchers have found that a persons consciousness does remain working after the body has died and ceased showing signs of life.
In other words, the person is aware that theyre dead. If that person is in a hospital room, he/she can even hear doctors announcing their death.

 Illustration – Shutterstock | l i g h t p o e t
Illustration – Shutterstock | l i g h t p o e tThere was a film released in the 90s called Flatliners, where five medical students deliberately stopped their hearts for short periods of time to experience the afterlife. Well, a team of researchers from New York University Langone School of Medicine also looked into that very same question.
The team studied patients who had been resuscitated in Europe and in the United States, who were brought back to life after suffering a cardiac arrest (or heart attack).
“Technically speaking, thats how you get the time of death—its all based on the moment when the heart stops,” NYUs director of critical care and resuscitation research, Dr. Sam Parnia, told Live Science. “Once that happens, blood no longer circulates to the brain, which means brain function halts almost instantaneously.”

 Illustration – Shutterstock | sfam_photo
Illustration – Shutterstock | sfam_photoHowever, according to Dr. Parnia, many of the resuscitated patients detailed experiences of hearing and seeing what was going on around them, even after they were pronounced dead.
“Theyll describe watching doctors and nurses working and theyll describe having awareness of full conversations, of visual things that were going on, that would otherwise not be known to them,” Dr. Parnia said.

 Illustration – Shutterstock | Tyler Olson
Illustration – Shutterstock | Tyler OlsonTheir stories were later verified by medical and nursing staff present on the scene. Dr. Parnia and his team are continually investigating what exactly happens after death.
“Were trying to understand the exact features that people experience when they go through death, because we understand that this is going to reflect the universal experience were all going to have when we die,” he added.
Dr. Parnia further mentioned: “At the same time, we also study the human mind and consciousness in the context of death, to understand whether consciousness becomes annihilated or whether it continues after youve died for some period of time—and how that relates to whats happening inside the brain in real time.”
Alluding to people who have faced a near-death experience, Dr. Parnia said, “What tends to happen is that people whove had these very profound experiences may come back positively transformed—they become more altruistic, more engaged with helping others. They find a new meaning to life having had an encounter with death.”
In an earlier study in 2013, researchers at the University of Michigan found that theres proof of a “burst of brain energy” as a person passes away.
These recent findings beckon some important questions—if the physical body is dead and has ceased to function, then how could a person still be conscious? Does this not prove that thought doesnt emanate from the brain, as suggested by scientists, but from a spiritual consciousness, akin to a soul, which is unrestricted by the body?
Watch the video:
[youtube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tHcZc-JJEFw?wmode=transparent&wmode=opaque&w=671&h=377] ]]> Canadian Polar Bear Population Thriving Despite Climate Change, Court Documents Claim https://www.theepochtimes.com/canadian-polar-bear-population-thriving-despite-climate-change-court-documents-claim_3137508.html Tue, 05 Nov 2019 14:39:32 +0000 Contrary to the popular narrative that the polar bear population is falling as a result of shrinking Arctic sea ice, Inuit groups claim the species is thriving, according to federal affidavits submitted in court.
“Inuit have not noticed a significant decline in the health of the polar bears,” the Nunavik Marine Region Wildlife Boards director of wildlife management wrote in court papers, reported Blacklocks Reporter.
“In fact Nunavik Inuit report that it is rare to see a skinny bear and most bears are observed to be healthy,” the affidavit read.
Inuit groups submitted the documents after Environment Canada called for hunting quotas of the polar bear to be slashed, citing “conservation concerns.”
According to the International Union for the Conservation of Nature, there are around 22,000 to 31,000 polar bears worldwide at present, and the bears are listed as a vulnerable species.
For years, organizations such as the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) have cited the predicted decline of the polar bear population as an inevitable consequence of global warming. It estimated that global polar bear numbers will fall by 30 percent by 2050.
Similarly, a 2016 study on global polar bear numbers estimated the the global polar bear population could decline by more than 30 percent in as little as 35 years. Researchers looked at the effect of climate change on the Arctic Ocean and calculated the likelihood of the projected population drop as 71 percent. Thats because polar bears stand on Arctic sea ice when hunting for seals.
However, the federal affidavits claim residents in Nunavik, northern Canada, have seen an increase in the polar bear population, and “a particularly notable increase since the 1980s.” Twelve of the worlds polar bear subpopulations are mainly found in the region.
The Nunavik Marine Region Wildlife Board report contains quotes from a hunter saying that polar bears are “not going extinct” and that there is no shortage.
The report read: “Many participants were very concerned about perspectives from outside Nunavik that polar bears are endangered elsewhere.”
“All interviews conducted in the Southern Hudson Bay communities shared the view the population grew somewhat from the 1960s until the 1980s, and that a continued increase has been very noticeable since that time.”
Controversial Viral Polar Bear Video
A polar bear monitor, Leo Ikakhik, explained that a viral video of a starving polar bear may not be what it seems.
“I wasnt totally surprised. These things happen,” he told the CBC. “Mother Nature is going to do part of that. You know, its just part of the cycle.”
The emaciated bear captured the attention of millions of people as it rummaged through trash to search for food.
“This is what climate change looks like,” said National Geographic.
Ikakhik has monitored bear activity around Arviat—a town on the western shore of the Hudson Bay—since 2010, and he works with organizations like World Wildlife Fund Canada to prevent the bears from coming near human populations.
“Everybody probably was shocked to see a really skinny bear, but this is not my first time seeing something like this,” he said.
He added to the CBC that it probably isnt climate change that caused the bear to appear that way.
“I wouldnt really blame the climate change. Its just part of the animal, what they go through,” he said.
“Since Im from the north, I wouldnt really fall for the video,” he added.
The bear was filmed by National Geographic photojournalist Paul Nicklen for conservation organization SeaLegacy.
“We are not sure that it was because of climate change. It is impossible to tell why he was in this state. Maybe it could have been an injury or a disease, but the point is that it was starving and we want people to know what a starving polar bear looks like, because as we lose the ice in the Arctic polar bears will starve,” SeaLegacy co-founder Cristina Mittermeier also noted.
]]> SpaceX Plans Launching 30,000 More Starlink Satellites to Meet Projected Internet Demands https://www.theepochtimes.com/spacex-plans-launching-30000-more-starlink-satellites-to-meet-projected-internet-demands_3136307.html Mon, 04 Nov 2019 05:16:10 +0000 The Space Exploration Technologies Corporation, SpaceX, is planning to send 30,000 new Starlink broadband satellites into the sky in a bid to meet future demands for fast and reliable internet, TechCrunch reports.
Elon Musks company recently filed the request with the International Telecommunication Union, which governs international use of global bandwidth. The proposal is anticipated to be affirmed soon, according to the report.
The company already has permission to launch 12,000 new satellites into space and hopes the extra satellites will responsibly “meet users anticipated needs.”
A SpaceX spokesperson told the publication: “As demand escalates for fast, reliable internet around the world, especially for those where connectivity is non-existent, too expensive or unreliable, SpaceX is taking steps to responsibly scale Starlinks total network capacity and data density to meet the growth in users anticipated needs.”
The publication says SpaceX is hoping to launch hundreds of satellites in the coming year as it anticipates a considerable demand for highly-optimized broadband globally.
However, the service will initially be provided to the northern U.S., as well as parts of Canada, from as early as next year, when the network goes live.
It will reportedly take up to 24 launches of Starlink satellites for SpaceX to be able to provide global coverage. It will not be operating all of its satellites in the same orbital region.
The company is also taking specific measures to avoid additional issues with traffic, such as building an automated collision avoidance system, structuring de-orbiting plans, and sharing information about the orbital routes of their satellites.
It is also said to be turning back around all the Earth-facing Starlink satellites to minimize reflected light. Astronomers and space watchers are worried that a build-up of satellites may impact scientific observation and research.
SpaceX said it is meeting or exceeding all of the industry standards that have been established so far.
Earlier this year, in May, the company deployed 60 of its Starlink satellites from its Falcon 9 rocket, which launched from Cape Canaveral in Florida.
On Tuesday, founder and CEO Musk appeared to have successfully sent a message using the Starlink network.
Posting on Twitter, he wrote: “Sending this tweet through space via Starlink satellite”, followed shortly by: “Whoa, it worked!!”
However, it has not been confirmed whether he did indeed use the Starlink satellite to send the tweet.
SpaceX was founded in 2002 by Elon Musk to reduce space transportation costs to enable the colonization of Mars.
]]> Do What Makes You Happy, Chemistry Nobel Prize Winner Says https://www.theepochtimes.com/the-nobel-prize-in-chemistry-goes-to-the-inventor-of-rechargeable-lithium-batteries_3130366.html Fri, 01 Nov 2019 06:11:23 +0000 BINGHAMTON, N.Y.—In the corner of the hall on the second floor of the Innovative Technologies Complex campus at Binghamton University, theres an office decorated with balloons. A modest way to celebrate Dr. M. Stanley Whittinghams 2019 Chemistry Nobel Prize.
Now 78 years old, Whittingham is still excited about batteries, visiting laboratories, and giving lectures around the globe.
“So people say, When are you going to retire?'” Whittingham said. And hell reply, “I like what Im doing. Im gonna keep doing it.”
And his wife, Dr. Georgina Whittingham, who is a professor of foreign languages, says the same.
“We keep teaching,” he said. “And my doctor says, Dont retire.'”
For more than 30 years, Whittingham has been working at Binghamton University in different positions. Currently, hes a distinguished professor of Chemistry and Materials Science and Engineering.
Its a place he loves.
“Theres a lot more teamwork here,” he said.
Hes a busy man—even more so since being announced as a key figure in history. What won him the Nobel Prize was that he was the first to develop the lithium battery in the 1970s at Exxon.
British at Heart
He came from a small town—Lincolnshire, England—where his high-school teacher got him excited about chemistry.
“Those days, you could make chemicals, blow things up, and things that you are not allowed to do,” he said with a laugh. “So I got excited about chemistry.”
He then made it to Oxford and finished his B.A., M.A., and Ph.D.
At the end of his Ph.D., unlike many colleagues who went to North America and Canada, he decided to go to Stanford University.
“I wanted to go somewhere with sunshine,” he said with a laugh. “Im still British at heart.”
After being there for two months, he was asked to take charge of the material labs of the Department of Defense for the next two years.
“Very successful time, I should say. During those two years, something even more important happened,” Whittingham said. “I met my wife at Stanford.”
“We didnt waste any time. Within, I think, nine months, we were married.”
Next-Generation Batteries
After finishing his postdoctoral research in two years, he went to work for Exxon.
“I was hired to work on energy, but not petroleum or chemicals,” he said.
With a keen interest in solar energy and fuel cells, he started researching batteries.
“We wanted to build the next-generation battery,” he said. “The big interest was electronic vehicles because of the gas crisis in the U.S.”
So they started building batteries in test tubes. At that time, they didnt have any unique environment, advanced machines, or even theories on what they might discover.
“We knew there was something there. We didnt know how big it would be.”
Whittingham never thought his invention would change the world.
“Even 15 years ago, the phone, youd need a whole briefcase to carry it. And I think lithium batteries helped all these little devices.”
In the 1980s, John Goodenough, using the foundation that Whittingham laid, made another breakthrough to even more powerful batteries.
With a physicists eyes, Goodenough set out to test something that they thought wouldnt work, Whittingham said.
Following that, in 1985, Akira Yoshino created the first commercially viable lithium-ion battery.
After decades, these three scientists who changed the world have been recognized with the 2019 Chemistry Nobel Prize.
And its all about perseverance.
“Youre going to make mistakes. Dont worry about that,” Whittingham said. “If you dont make mistakes, you wont make the big breakthrough.”
After working for Exxon, Whittingham realized research and academia was something he always wanted to come back to.
Young at Heart
Whittingham took up a professorship at Binghamton University in the late 80s and continued his research on batteries.
“I really wanted to do research, because lots of academia you get 18-year-olds every year coming in. So it keeps you younger,” he said jokingly.
But in the end, he said what matters is that he does what he likes.
“I think youre successful if youre happy with what youre doing,” he said. Winning a prize certainly helps as well, he said with a laugh.
“Its so motivating that, even at his age, hes still young,” said Anshika Goel, one of his Ph.D. students. “He comes in the lab, he comes to the office every day on time, no matter how much hes traveling.”
“He just replied [to] my email at 3 a.m.; hes still working,” said Yicheng Zhang, another of Whittinghams Ph.D. students.
Now, 30 years later, hes still teaching, and its his passion that keeps him young at heart.
]]> Hsinchu Science Park Bureau Hosts Biotech Fair in Japan to Extend Bilateral Ties for Taiwanese Biomedical Manufacturers https://www.theepochtimes.com/hsinchu-science-park-bureau-hosts-biotech-fair-in-japan-to-extend-bilateral-ties-for-taiwanese-biomedical-manufacturers_3131958.html Wed, 30 Oct 2019 18:43:18 +0000 A biotech delegation organized by Metal Industries Research and Development Centre and six high-tech medical equipment manufacturers (Medimaging Integrated Solution, Brain Navi Biotechnology Co, Advanced Biomedical Technology, General Biologicals Corporation, North-vision Technology, and Phalanx Biotech Group), led by Deputy Director-General Shu-Chu Chen of the Hsinchu Science Park Bureau, Ministry of Science and Technology, went to Tokyo for a business matching fair on Oct. 23, 2019.
To enhance bilateral business ties and extend mutual market niches, the matching fair provided a one-on-one forum on Oct. 24. Participants of the fair from Japan included more than 10 Japanese companies from business and social care organizations.
Participants of the fair gave positive feedback on the bilateral interaction.
Doctor Nakagawa Shiro, also a member of the WTO Trade Dispute Resolution Committee and a distinguished Professor of Nagoya City University, expressed that the event held the most successful and terrific interaction he has ever seen between Japan and Taiwan.


Delegates from the Hsinchu Science Park included companies engaged in medical devices such as digital medicine, medical imaging, 3D printing, precision medicine, and precision detection.


Companies in Japan that participated in the fair included manufacturers of shock sensors, medical imaging information, in vitro testing, clinical reagents, pharmaceutical services, frontend components, and venture capital firms.
The participating companies gained potential business opportunities for further interactions.
The Hsinchu Science Park Bureau also hosted a bilateral interaction banquet on the evening of Oct. 24 to enhance Japan-Taiwan business ties.
Deputy Director-General Chen of the Hsinchu Science Park Bureau stated that Taiwans medical device industry has grown rapidly in recent years and has gained a global reputation for product quality and technical features which including global renowned journals and media.
Forbes and the World Economic Forum report that Taiwan is a global leader in medical care and health technologies. The Hsinchu Science Park exhibits its competitive advantages in semiconductor industry technologies, embarking on diversified cross-domain high-end medical devices and technologies such as minimally invasive devices, smart aid systems, brilliant image processing, and intelligent diagnosis systems, which have attracted international and domestic counterparts.
High-tech features at the Hsinchu Science Park, including IC design, semiconductor manufacturing, information, optoelectronics, and telecommunications, have turned out to be crucial drivers for the next generation of innovative healthcare devices.
The collaborative fair provided biomedical device industries from the Hsinchu Science Park in-depth interactions with Japanese companies, building bilateral supply chains for further progress and collaborations, resulting in a win-win outcome.
Sponsored by Hsinchu Science Park (HSP), Ministry of Science and Technology
]]> Chinas Ocean Waste Surges 27% in 2018: Ministry https://www.theepochtimes.com/chinas-ocean-waste-surges-27-in-2018-ministry_3130624.html Tue, 29 Oct 2019 15:45:45 +0000 BEIJING/SHANGHAI—China dumped a total of 200.7 million cubic meters of waste into its coastal waters in 2018, a 27 percent rise on the previous year and the highest level in at least a decade, the countrys environment ministry said on Oct. 29.
The majority of the waste was dumped in the delta regions of the Yangtze and Pearl rivers, both major industrial zones on Chinas eastern coast, the Ministry of Ecology and Environment (MEE) said.
“At the moment, there are some clear problems with the work on the marine ecological environment, with some regions not showing a lot of awareness or paying sufficient attention, and lacking strong initiative and dedication,” Huo Chuanlin, deputy director of the MEEs marine environment department, said at a briefing in Beijing.
Environmental groups have expressed concern that China, desperate to clean up its own rivers, is dumping increasing amounts of trash in its seas instead.
Of the 8.8 million tons of plastic waste that flows down the worlds “small first order streams to large rivers that discharge to the sea,” the “top ten” polluting rivers account for 88-95 percent of plastics that flow each year into the worlds oceans.
The six Chinese rivers on the “top ten” list—the Yangtze, Yellow, Hai, Pearl, the Amur that borders Russia, and the headlands of the Mekong River—account for about 3.8 million tons, or almost half of the worlds plastic flow into the oceans. The Yangtze alone accounts for 1.6 million tons of plastic discharged into the oceans.
China found an average of 24 kilograms of floating trash per 1,000 square meters of surface water last year, 88.7 percent of which was plastic, the ministry said. Plastic also dominated the waste found below the surface, including on the seabed.
Earlier this year, Beijing published an action plan designed to clean up the Bohai Bay, one of the countrys busiest and most polluted waterways.
China has earmarked 7 billion yuan ($991.70 million) for the clean-up this year alone, but Huo said it is still expected to struggle to meet a key target aimed at making at least 73 percent of Bohai waters fit for human contact by next year, up from around 70 percent at present.
China is planning to make around 30 percent of its coastal waters completely off-limits to development as part of a national “ecological red line” scheme.
But it is also trying to protect its rivers and improve the environment of its cities by moving polluting industries like steel and petrochemicals to the coast.
By Muyu Xu and David Stanway. Epoch Times contributor Chriss Street contributed to this report.
]]> Secretive Military Spaceplane Lands in Florida After Record-Long Orbital Flight https://www.theepochtimes.com/secretive-military-spaceplane-lands-in-florida-after-record-long-orbital-flight_3129424.html Mon, 28 Oct 2019 10:10:54 +0000 WASHINGTON—The Pentagons secretive X-37B spaceplane landed in Florida on Sunday after a record-long orbital flight lasting more than two years, the U.S. Air Force said. It caps the latest test mission for an array of military technologies.
The unpiloted X-37B, built by Boeing Co., touched down on an airstrip at NASAs Kennedy Space Center at 3:51 a.m. ET after spending 780 days orbiting Earth as the Air Forces fifth flight mission under the Orbital Test Vehicle program, the Air Force said.
The spaceplane, roughly the size of a small bus and sharing many design features with NASAs Space Shuttle, was sent into orbit in 2017 atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. The mission was managed by the Washington-based Air Force Rapid Capabilities Office to conduct various classified technology experiments in a long-duration space environment.
“The X-37B continues to demonstrate the importance of a reusable spaceplane,” Barbara Barrett, the newly appointed Air Force secretary, said in a statement. “Each successive mission advances our nations space capabilities.”
The previous X-37B mission lasted 718 days and landed in 2017. Sunday mornings landing tallies 2,865 total days for the program overall, the Air Force said.
The Pentagon, increasingly reliant on space technologies, recently created the U.S. Space Command and is asking Congress to approve funding for a proposed Space Force, which would serve as a new branch of the military.
“The sky is no longer the limit for the Air Force and, if Congress approves, the U.S. Space Force,” General David L. Goldfein, Chief of Staff of the Air Force, said.
By Joey Rouelette
]]> Dutch Inventor Unveils Device to Scoop Plastic From Rivers https://www.theepochtimes.com/dutch-inventor-unveils-device-to-scoop-plastic-from-rivers_3129116.html Mon, 28 Oct 2019 09:34:35 +0000 ROTTERDAM, Netherlands—Dutch inventor Boyan Slat is widening his effort to clean up floating plastic from the Pacific Ocean by moving into rivers, too, using a new floating device to catch garbage before it reaches the seas.
The 25-year-old university dropout founded The Ocean Cleanup to develop and deploy a system he invented when he was 18 that catches plastic waste floating in the ocean.
On Oct. 26, he unveiled the next step in his efforts: A floating solar-powered device that he calls the “Interceptor,” which scoops plastic out of rivers as it drifts past.
“We need to close the tap, which means preventing more plastic from reaching the ocean in the first place,” he said, calling rivers “the arteries that carry the trash from land to sea.”
Slats organization has drawn criticism in the past for focusing only on the plastic trash already floating in the worlds oceans.
Experts say that some 9 million tons of plastic waste, including plastic bottles, bags, toys, and other items, flow annually into the ocean from beaches, rivers, and creeks.
Three of the machines are already deployed to Indonesia, Malaysia, and Vietnam—with a fourth heading to the Dominican Republic, he said.
Izham Hashim from the government of Selangor state in Malaysia was present at the launch and said he was happy with the machine.
“It has been used for one and a half months in the river and its doing very well, collecting the plastic bottles and all the rubbish,” he said.
Slat said he believes 1,000 rivers are responsible for some 80 percent of plastic pouring into the worlds oceans, and he wants to tackle them all in the next five years.
“This is not going to be easy, but imagine if we do get this done,” he told an audience of enthusiastic supporters, who whooped, clapped, and cheered at his announcement. “We could truly make our oceans clean again.”
The vessel is designed to be moored in rivers and is shaped to deflect larger floating debris such as tree trunks.
He used his live-streamed unveiling to seek the support of countries committing to clean up their rivers, and businesses that are prepared to inject funding and help with the operation of the devices.
The interceptors work by guiding plastic waste into an opening in its bow. A conveyor belt then carries the trash into the guts of the machine, where its dropped into dumpsters. The interceptor sends a text message to local operators to empty it when its full.
Slat demonstrated the device by dumping hundreds of yellow rubber ducks into the water at the launch event in Rotterdams port. The interceptor caught nearly all of them.
The machines currently cost about 700,000 euros ($775,600), but Slat said the cost will likely drop as production increases.
Jan van Franeker of the Wageningen Marine Research Institute has been critical of The Ocean Cleanup in the past, but said the new device looks promising.
“I am really happy they finally moved toward the source of the litter,” he said in a telephone interview. “The design, from what I can see, looks pretty good.”
Slat said the economic impact of not picking plastic out of rivers is higher than the cost of buying and using the machines.
“Deploying interceptors is even cheaper than deploying nothing at all,” he said.
By Mike Corder
]]> Critics Analyze EPA Fuel Standards as California Continues Political Battle With Trump Over Regulations https://www.theepochtimes.com/critics-analyze-epa-fuel-standards-as-california-continues-political-battle-with-trump-over-regulations_3125536.html Wed, 23 Oct 2019 18:34:55 +0000 The Trump Administration announced in September their decision to withdraw Californias waiver from the 2013 Clean Air Act.
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Administrator Andrew Wheeler and Transportation Secretary Elaine Chao stated that the EPA is finalizing the “One National Program Rule” regarding fuel standards.
A press release by the EPA stated that the policy will “enable the federal government to provide nationwide uniform fuel economy and greenhouse gas emission standards for automobiles and light duty trucks.”
The decision will remove Californias authority to set its own fuel emission standards which are currently higher than national standard.
“Todays action meets President Trumps commitment to establish uniform fuel economy standards for vehicles across the United States, ensuring that no state has the authority to opt out of the nations rules, and no state has the right to impose its policies on the rest of the country,” said Chao during the press conference.
Many people are concerned that the new policy will lead to negative effects on the planet, arguing that stricter fuel emission policies will help protect the air and environment.
The Epoch Times reached out to Sterling Burnett, a senior fellow on environmental and energy policy at The Heartland Institute, to discuss the new EPA decision and its effects on the country.
Regarding the concern of increasing levels of carbon dioxide, Burnett explained that “there is no question that there could be some level where it [carbon dioxide] is dangerous, but we are nowhere near that and nothing that this [decision] does, Trumps decision to freeze standards where they are, will not raise levels of carbon dioxide appreciably.”
According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), “the global average atmospheric carbon dioxide in 2018 was 407.4 parts per million,” which is the highest levels have been in the past 800,000 years.
Burnett noted that carbon dioxide is a necessary gas for plants to live and thrive. Without carbon dioxide, among other nutrients, plants will be unable to produce oxygen or food for itself, but balance is key.
Political Battle
However, while environmental concerns are important, the problem with the previous 2013 Clean Air Act is that it allowed California, as the sole state, to set the national standard for fuel emissions.
Burnett said that California and the 22 other states suing the Trump administration have incorrectly claimed that the new decision is rolling back and lowering the nationwide fuel emission standards.
“What Trump is doing is not rolling back standards, he is simply freezing standards where they currently are,” Burnett explained.
Individual states do not have the power or right to set nationwide policies. The current proposal under the Trump Administration is simply pushing for a uniform nationwide standard.
Another problem with the 2013 Clean Air Act is that it essentially limits peoples freedom of choice in deciding on the type of vehicles they can own.
Because Californias fuel standards are higher than the national standard, car producers are forced to produce vehicles according to Californias standards to reduce the cost of production.
If California continues to set the standard, “by de facto, what will happen is, car manufacturers will say we want to sell cars in California and other states that have adopted Californias standards. Were not going to produce two sets of cars. What it means is that everyone will have to live with the cars that California allows, which is electric vehicles, small vehicles, not light trucks, not mini vans, not sedans,” Burnett said.
For California, the opposition toward the EPAs decision is more of a political battle rather than a concern for the environment.
“The reality is California needs stricter standards because of high population density. Many Californians remember how bad smog was in LA over 50 years ago. So why cant California work with the federal government to find a solution? Because of California Democrats war with President Trump,” said Konstantinos Roditis, former 2018 election candidate for California State Controller.
]]> Interstellar Interloper Is a Comet Resembling Those in Our Solar System https://www.theepochtimes.com/interstellar-interloper-is-a-comet-resembling-those-in-our-solar-system_3116352.html Mon, 14 Oct 2019 21:55:28 +0000 The second interstellar object ever spotted passing through the solar system is a comet that appears quite like those formed in our neighborhood of the cosmos, providing fresh evidence that other planetary systems may be very similar to our own.
Astronomers on Monday provided some of the first details about the comet now hurtling toward the sun, saying it has a solid nucleus with a radius of about six-tenths of a mile (1 km), a cloud-like structure of dust and gas emitted by the nucleus, the telltale tail of a comet and a reddish color.
First detected in August by an amateur astronomer named Gennady Borisov, it is called 2I/Borisov. The only previous interstellar visitor discovered in our solar system was a cigar-shaped rocky object called Oumuamua found in 2017.
The comet was studied using telescopes in Hawaii and Spain.
“Its properties determined so far—morphology, color, estimated size—are remarkably similar to the native solar system comets. This is important because it shows that comets exist in interstellar space, confirming long-standing predictions, and it tells us that comets similar to the ones we know from this solar system also form around other stars,” said astronomer Michal Drahus of Jagiellonian University in Poland.
Both 2I/Borisov and Oumuamua formed in other planetary systems and were ejected by gravitational perturbations into interstellar space as orphans wandering the cosmos.
“Our Solar System is regularly visited by escapees from other planetary systems, and it has always been this way. Its just that we havent been able to detect them until recently,” Drahus said.
The speed of 2I/Borisov and the nature of its orbital path demonstrated that it did not originate in our solar system, Jagiellonian University astronomer Piotr Guzik said. Guzik added that he expects that within a decade or so a space probe will be sent from Earth to visit an interstellar object.
“I think this is the most important and transformative moment for planetary astronomy since the discovery of the first exoplanets (planets in other star systems) in the early 1990s and a milestone for astronomy in general. Interstellar minor bodies are this long-sought bridge between other planetary systems and our own solar system. I like to think of them as miniature exoplanets in our own cosmic backyard,” Drahus said.
The comet is expected to reach its closest point to the Sun on Dec. 8 and its closest point to the Earth soon thereafter, coming within about 186 million miles (300 million km) of our planet. By way of comparison, the moon orbits about 240,000 miles (386,000 km) from Earth.
The research was published in the journal Nature Astronomy.
By Will Dunham
]]> Saturn Is the Solar Systems Moon King, With 20 More Spotted https://www.theepochtimes.com/saturn-is-the-solar-systems-moon-king-with-20-more-spotted_3112438.html Thu, 10 Oct 2019 13:01:03 +0000 Saturn is now being recognized as the “moon king” of our solar system, with astronomers spotting 20 more of them orbiting the giant ringed planet, bringing its total count to 82—three more than Jupiter.
The newly identified small moons, ranging from about 2 to 4 miles (3 to 6 km) in diameter, were detected using the Subaru telescope in Hawaii by a research team led by astronomer Scott Sheppard of the Carnegie Institution for Science in Washington.
“Saturn is the moon king,” Sheppard said on Oct. 9 in an email interview.
The discovery was announced this week by the International Astronomical Unions Minor Planet Center.
One of the moons orbits at an astounding distance of about 15 million miles (24 million km) from Saturn, farther away than any of its other moons. By comparison, Earths moon orbits about 240,000 miles (386,000 km) from the planet.
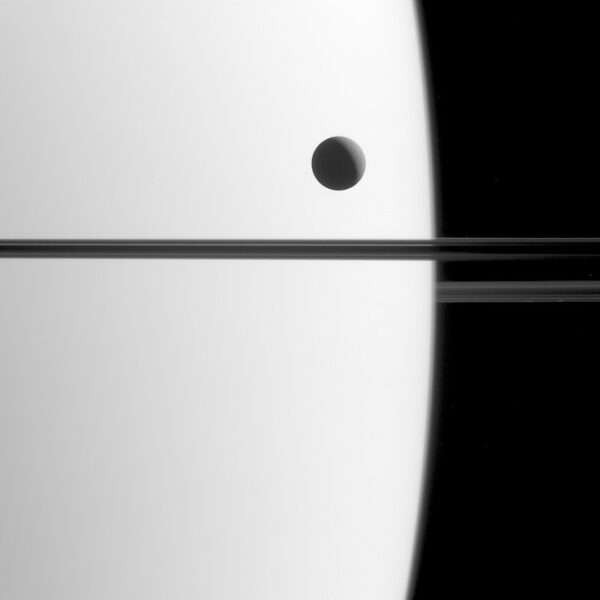


Seventeen of the newly detected Saturnian moons are orbiting in the opposite direction of the planets rotation. The other three orbit in the same direction Saturn spins, as is typically the case.
A number of the moons appear to be fragments of once-larger moons that broke up in long-ago collisions with other moons or passing comets or asteroids, Sheppard said. That is similar to some of the 79 moons orbiting Jupiter.
Saturn, a gas giant made up mostly of hydrogen and helium, is the second-largest planet in the solar system and the sixth from the sun. Its diameter of about 72,000 miles (116,000 km) dwarfs Earth diameter of about 7,900 miles (12,700 km).
Only Jupiter, the fifth planet from the sun, is larger.

“These new moons show us the solar system was a very chaotic place in the distant past, with objects flying all over the place. These are the last remnants of the objects that formed in the giant planet region, as all of the other objects that formed in this region have either been ejected or incorporated into the planets themselves,” Sheppard said.
The newly identified moons are much smaller than Saturns largest, the icy world Titan, whose diameter of about 3,200 miles (5,150 km) exceeds that of the innermost planet, Mercury.
“We believe Saturn likely has about 100 moons larger than one mile (1.6 km), but the discovery of these new moons that are about two to four miles in size is pushing the limit of our current ability to find them. We will need the next generation of large telescopes to find smaller moons,” Sheppard added.
By Will Dunham
]]> Battery Pioneers Who Made Mobile Revolution Possible Win Nobel Chemistry Prize https://www.theepochtimes.com/battery-pioneers-who-made-mobile-revolution-possible-win-nobel-chemistry-prize_3111221.html Wed, 09 Oct 2019 14:25:31 +0000 Three scientists have won the 2019 Nobel Prize for Chemistry for putting power in peoples pockets by developing rechargeable lithium-ion batteries which made the global information technology, mobile and fossil-fuel-free revolutions possible.
American John Goodenough, at 97, became the oldest winner of a Nobel prize and shares the 9 million Swedish crown ($906,000 award equally with Stanley Whittingham from Britain and Akira Yoshino of Japan, the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences Nobel Committee said on Oct. 9.
“Lithium-ion batteries have revolutionised our lives since they first entered the market in 1991. They have laid the foundation of a wireless, fossil fuel-free society, and are of the greatest benefit to humankind,” the committee said.
With peals of infectious laughter, Goodenough asked reporters at a hastily called news conference in London to speak up with their questions so that his “old ears” could hear.
He had not been expecting to win a Nobel prize, he said, but was “very happy” to get it.
“Life is full of surprises,” he said after popping a bottle of champagne in celebration.
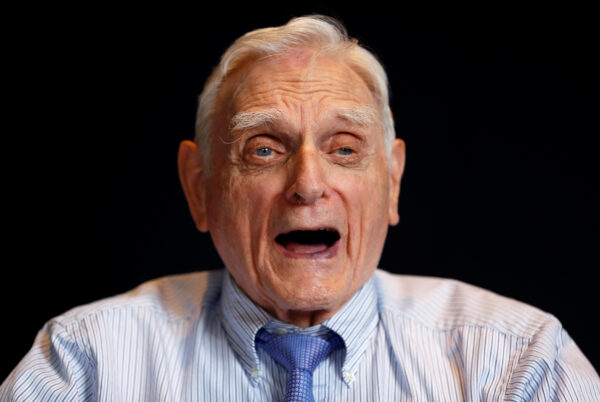


After Whittingham developed the first functional lithium battery in the early 1970s, Goodenough doubled the batterys potential in the following decade. Yoshino then eliminated pure lithium from the battery, making it much safer to use.
Helping The Environment
Speaking on Japanese TV after hearing of his win, a smiling Yoshino said he was glad to have helped the environment.
“I am happy that the lithium-ion battery won the prize in that context,” he said, adding that he also hoped it would inspire others: “I hope this will become an encouragement for young researchers.”
Gregory Offer, an expert in mechanical engineering at Imperial College London, said the scientists work had led to “one of the key enabling technologies of the 21st century”.
“They have already underpinned the mobile revolution, and are now essential to help us solve the problem of climate change by electrifying transport and storing renewable electricity generation,” he said in an emailed comment.


Paul Coxon, a materials science expert from Britains Cambridge University, said lithium-ion batteries were now “the hidden workhorses of the mobile era”.
“All three Nobel winners played vital roles in this energy storage revolution which has now placed power in our pockets,” he said. “Its a wonderful example of taking research from the lab. We can literally hold the result in our hands.”
The prizes for achievements in science, literature and peace were created and funded in the will of Swedish dynamite inventor and businessman Alfred Nobel and have been awarded since 1901.
The Nobel prizes for medicine and physics were awarded earlier this week. The awards for literature, peace and economics will be announced in the next few days.
Click for the Graphic of Nobel Laureates
By Niklas Pollard and Kate Kelland
]]> 3 Win Nobel Prize in Physics for Work to Understand Cosmos https://www.theepochtimes.com/3-win-nobel-prize-in-physics-for-work-to-understand-cosmos_3109817.html Tue, 08 Oct 2019 13:42:03 +0000 STOCKHOLM—A Canadian-American cosmologist and two Swiss scientists won this years Nobel Prize in Physics on Tuesday for their work in understanding how the universe has evolved from the Big Bang and the blockbuster discovery of the first known planet outside our solar system.
Canadian-born James Peebles, 84, of Princeton University, was credited for “theoretical discoveries in physical cosmology” and Switzerlands Michel Mayor, 77, and Didier Queloz, 53, each from the University of Geneva, were honored for discovering “an exoplanet orbiting a solar-type star,” said Prof. Goran Hansson, secretary general of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences.
Peebles, hailed as one of the most influential cosmologists of his time, will collect one half of the 9-million kronor ($918,000) cash award, and the Swiss men will share the other half.
The Nobel committee said Peebles theoretical framework about the cosmos—and its billions of galaxies and galaxy clusters—amounted to “the foundation of our modern understanding of the universes history, from the Big Bang to the present day.”


His work set the stage for a “transformation” of cosmology over the last half-century, using theoretical tools and calculations that helped interpret traces from the infancy of the universe, the committee said. Peebles is the Albert Einstein Professor of Science at Princeton.
Mayor and Queloz were credited having “started a revolution in astronomy” notably with the discovery of exoplanet 51 Pegasi B, a gaseous ball comparable with Jupiter, in 1995—a time when, as Mayor recalled—that “no one knew whether exoplanets existed or not.”
An exoplanet is a planet outside the solar system.
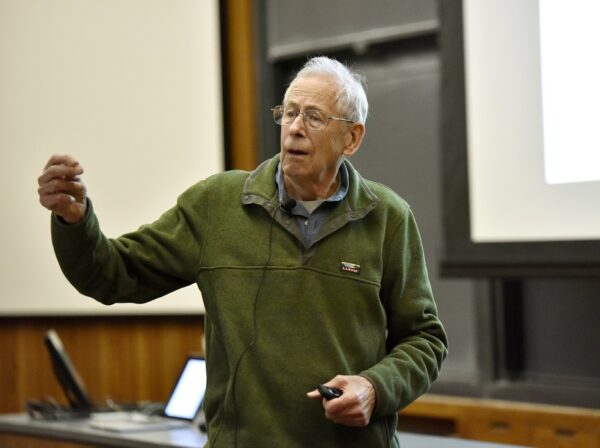


“Prestigious astronomers had been searching for them for years, in vain!” Mayor quipped.
More than 4,000 exoplanets have since been found in the Milky Way since then, and “Strange new worlds are still being discovered, with an incredible wealth of sizes, forms and orbits,” the committee said.
The University of Geneva quoted Mayor and Queloz as saying it was “simply extraordinary” that they won the prize for “the most exciting” discovery of their careers.


The cash prize comes with a gold medal and a diploma that are received at an elegant ceremony in Stockholm on Dec. 10, the anniversary of the death of prize founder Alfred Nobel in 1896, together with five other Nobel winners. The sixth one, the peace prize, is handed out in Oslo, Norway on the same day.
This was the 113th Nobel Prize in Physics awarded since 1901, of which 47 awards have been given to a single laureate. Only three women have been awarded it so far: Marie Curie in 1903, Maria Goeppert-Mayer in 1963 and Donna Strickland in 2018, according to the Nobel website.
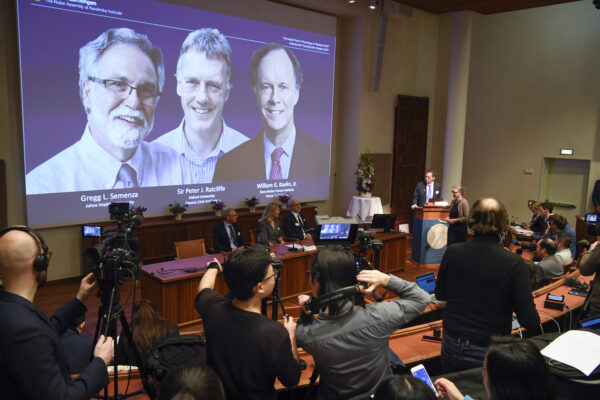
On Monday, Americans William G. Kaelin Jr. and Gregg L. Semenza and Britains Peter J. Ratcliffe won the Nobel prize for Physiology or Medicine, for discovering details of how the bodys cells sense and react to low oxygen levels, providing a foothold for developing new treatments for anemia, cancer and other diseases.


Nobel, a Swedish industrialist and the inventor of dynamite, decided the physics, chemistry, medicine and literature prizes should be awarded in Stockholm, and the peace prize in Oslo.
The Nobel Prize for Chemistry will be announced Wednesday, two Literature Prizes will be awarded on Thursday, and the Peace Prize comes Friday. This year will see two literature Prizes handed out because the one last year was suspended after a scandal rocked the Swedish Academy.
By David Keyton
]]> 3 Win Nobel Prize for Showing How Cells Sense Low Oxygen https://www.theepochtimes.com/3-win-nobel-prize-for-showing-how-cells-sense-low-oxygen_3109273.html Tue, 08 Oct 2019 05:40:50 +0000 NEW YORK—Two Americans and a British scientist won a Nobel Prize on Oct. 7 for discovering details of how the bodys cells sense and react to low oxygen levels, providing a foothold for developing new treatments for anemia, cancer, and other diseases.
Drs. William G. Kaelin Jr. of Harvard University, Gregg L. Semenza of Johns Hopkins University and Peter J. Ratcliffe at the Francis Crick Institute in Britain and Oxford University won the prize for advances in physiology or medicine.
The scientists, who worked largely independently, will share the 9 million kronor ($918,000) cash award, said the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm.
They “revealed the mechanism for one of lifes most essential adaptive processes,” the Nobel committee said.
Cells can encounter lowered oxygen not only from situations like living at high altitudes, but also from things like a wound that interferes with local blood supply. Their response triggers reactions that include producing red blood cells, generating new blood vessels and fine-tuning the immune system.
The Nobel committee said scientists are focused on developing drugs that can treat diseases by either activating or suppressing the oxygen-sensing machinery. Such manipulation could help in attacking cancer cells, experts said.
Another payoff is pills to boost the production of red blood cells in anemia, which can appear in people with chronic kidney disease. One such drug has been approved in China and Japan and a filing for approval in the U.S. is expected soon, Kaelin said.
Still other potential targets include heart attack and stroke, and a condition of reduced blood flow in the limbs that can lead to amputation, the researchers said.
Kaelin, 61, said he was half-asleep when the phone rang early Oct. 7 with the news of his award.
“I dont usually get phone calls at 5:00 in the morning, so, naturally, my heart started racing and I could see the call was from Stockholm,” he said. “And so I think at that point I almost had an out-of-body type of experience.”
Kaelin is paid by the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, which also supports APs Health and Science department.
Ratcliffe, 65, said he learned the news after he was summoned out of a meeting this morning by his secretary, who had “a look of urgency.”
Trained as a kidney specialist, Ratcliffe said his research began when he and colleagues simply wanted to figure out how cells sense oxygen.
“I thought it was a definable problem and just thought wed find out how it worked,” he said. It was about two years into their research program, which began in 1990, that they realized the discovery had much wider significance, Ratcliffe said.
“We saw that it wasnt just cells in the kidney that know how to sense oxygen, but all cells in the body. … There are hundreds and thousands of processes the body uses to adapt to and regulate its oxygen levels.”
He said while some promising drugs have been developed, it will be years before its clear whether such discoveries are going to change the lives of tens of thousands.
In Baltimore, Semenza, 63, said he slept through the Nobel committees initial phone call. “By the time I got to the phone it was too late,” he said. He went back to sleep but was able to answer the second call from Stockholm.
He said kidney cancer may be the first malignancy in which a drug based on the prize-winning work might make chemotherapy more effective, and that he hopes many other cancers will follow.
Speaking at a news conference at Johns Hopkins Universitys School of Medicine, Semenza paid tribute to his biology teacher, Rose Nelson, at Sleepy Hollow High School in Sleepy Hollow, N.Y., for inspiring his pursuit of medicine.
“She used to say, Now when you win your Nobel Prize, I dont want you to forget that you learned that here,'” he said. “Its my great sadness that she is not still alive to share the moment because I know it would have meant a lot to her. She was my inspiration.”
“Thats the importance of teachers,” he added. “To make that kind of spark.”
Steven McKnight of the UT Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas noted that the process discovered by the three researchers is widespread in the animal kingdom, found even in the worm. He said the honored work is “of a heroic nature.”
Last year, James Allison of the United States and Tasuku Honjo of Japan won the 2018 Nobel Prize for Medicine for their work in immunotherapy, activating the bodys natural defense system to fight tumors.
The Oct. 7 announcement kicked off this years Nobel Prizes. The physics prize will be handed out Oct. 8, followed by the chemistry prize on Oct. 9. This year there is a double-header for the Nobel Literature Prize—one each for 2018 and 2019—which will be awarded Oct. 10. The Peace Prize will be announced on Oct. 11.
The 2018 Nobel Literature prize was suspended after a sex abuse scandal rocked the Swedish Academy, the body that awards the literature prizes, so two prizes are being awarded this year.
The economics prize will be awarded Oct. 14. Officially known as the Bank of Sweden Prize in Economic Sciences in Memory of Alfred Nobel, it wasnt created by Nobel, but by Riksbanken, Swedens central bank, in 1968.
The laureates will receive their awards at elegant ceremonies in Stockholm and Oslo on Dec. 10—the anniversary of Nobels death in 1896.
]]> Three Scientists Awarded With Nobel Medicine Prize for Learning How Cells Use Oxygen https://www.theepochtimes.com/three-scientists-awarded-with-nobel-medicine-prize-for-learning-how-cells-use-oxygen_3108523.html Mon, 07 Oct 2019 14:50:06 +0000 LONDON—Two Americans and a British scientist won the 2019 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine for discovering how the bodys cells sense and react to oxygen levels, work that has paved the way for new strategies to fight anemia, cancer and other diseases, the Nobel Committee said.
Drs. William G. Kaelin Jr. of Harvard University, Gregg L. Semenza of Johns Hopkins University and Peter J. Ratcliffe at the Francis Crick Institute in Britain and Oxford University will share equally the 9 million kronor ($918,000) cash award, the Karolinska Institute said.
It is the 110th prize in the category that has been awarded since 1901.
Their work has “greatly expanded our knowledge of how physiological response makes life possible,” the committee said, explaining that the scientists identified the biological machinery that regulates how genes respond to varying levels of oxygen.
That response is key to things like producing red blood cells, generating new blood vessels and fine-tuning the immune system.

The Nobel Committee said scientists are focused on developing drugs that can treat diseases by either activating or blocking the bodys oxygen-sensing machinery.
The oxygen response is hijacked by cancer cells, for example, which stimulate formation of blood vessels to help themselves grow. And people with kidney failure often get hormonal treatments for anemia, but the work of the new laureates points the way toward new treatments, Nils-Goran Larsson of the Nobel committee told The Associated Press.
Reached at his home, Kaelin said he was half-asleep Monday morning when the phone rang. It was Stockholm.
“I was aware as a scientist that if you get a phone call at 5 a.m. with too many digits, its sometimes very good news, and my heart started racing. It was all a bit surreal,” he said.
Kaelin said he isnt sure yet how hell spend the prize money but “obviously Ill try to put it to some good cause.” Kaelin is paid by the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, which also supports APs Health and Science Department with some grants.
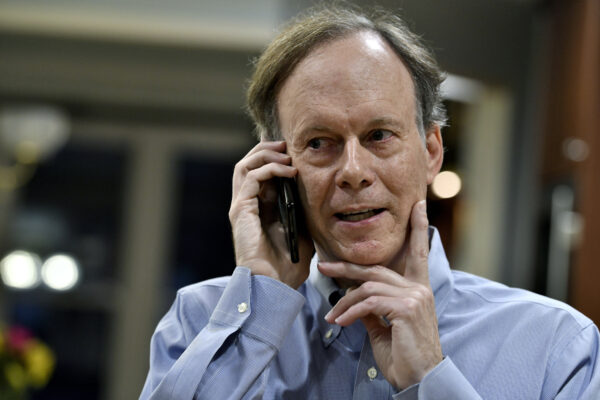


Ratcliffe said he was summoned out of a meeting this morning by his secretary, who had “a look of urgency.”
“He had a Swedish accent, so I figured it probably wasnt one of my friends pulling my leg,” he said of the Nobel caller.
Trained as a kidney doctor, Ratcliffe said his research began when he and colleagues simply wanted to figure out how cells sense oxygen.
“I thought it was a definable problem and just thought wed find out how it worked,” he said. Ratcliffe said it was about two years into the research program that first began in 1990 when they realized the discovery had much wider significance.
“We saw that it wasnt just cells in the kidney that know how to sense oxygen, but all cells in the body,” he said. “They use this to do a huge range of other things, reprogram the cells, cause the growth of blood vessels, differentiation of cells. There are hundreds and thousands of processes the body uses to adapt to and regulate its oxygen levels.”
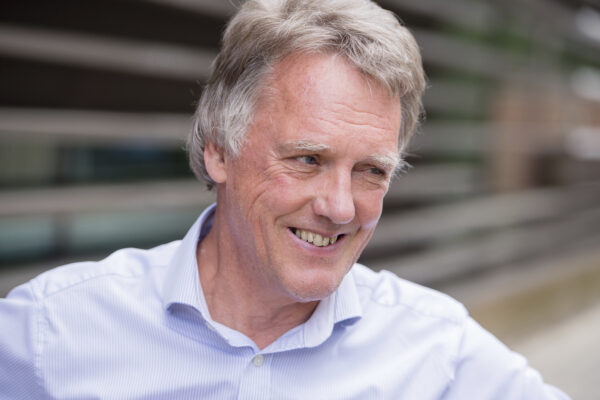


He said while some promising drugs have been developed, including for kidney patients who dont get enough oxygen, it will be years before its clear whether such discoveries are going to change the lives of tens of thousands.
Ratcliffe described his fellow laureates as “colleagues, competitors and friends.” He said felt honored by the Nobel accolade but that his main goal had always been pure science.
“The satisfaction is really finding things out that will continue to be true for all time,” he said. “This is for me an eternal truth and as a scientist, we work away, we find these things out and we hope they will be useful.”
Ratcliffe said he plans to have a celebratory party at the laboratory and later with his family. “A lot of people came to the office after the phone call and we had some champagne,” he said.
In Baltimore, Semenza said it was when he and colleagues were studying a gene in a rare cell type in the kidney and they did an experiment that showed the factor they discovered—which was linked to oxygen—that suggested it had widespread physiological importance. It turns out that the gene turns on erythropoietin, or EPO, which controls red blood cell production, when cells dont get enough oxygen.
“We found it very interesting that the body can respond to oxygen,” he told the AP. That discovery has led to treatments for people with chronic kidney disease who become anemic when their kidneys stop making EPO. “Now, drugs can turn on EPO production by increasing these factors.”
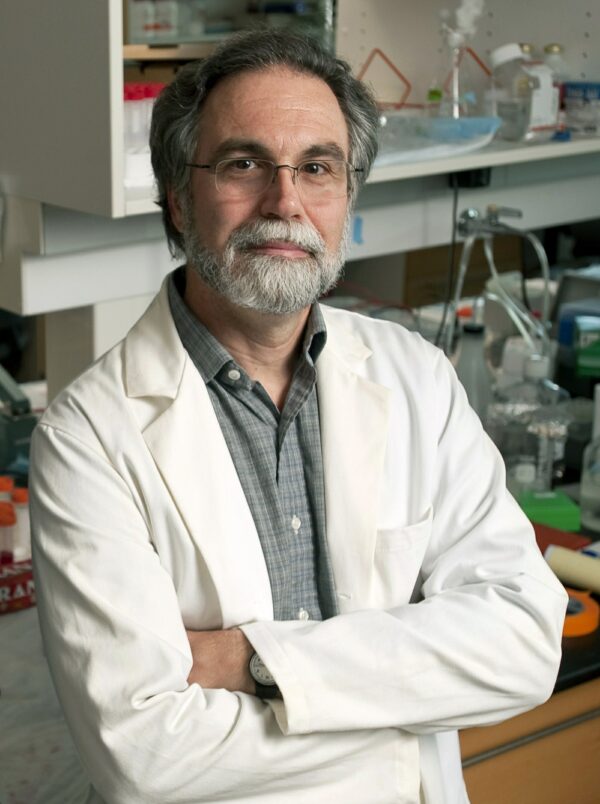


Semenza said it was likely one or more of these drugs will be approved for production in the next few years and that one has already been green-lighted in China.
Semenza has gone on to author more than 400 research articles and book chapters.
Andrew Murray of the University of Cambridge said the three laureates discovery was fundamental to understanding how to combat diseases of the heart and lungs as well as numerous cancers.
“Low oxygen levels are a feature of some of the most life-threatening diseases,” he said. “When cells are short of oxygen, as is the case with heart failure and lung disease, the tissues need to respond to that in order to maintain energy levels.”
Murray said the case of cancer was slightly different. Some cancer tumors thrive under low oxygen conditions, so Murray said scientists are trying to develop drugs to manipulate oxygen levels under these circumstances.
“The work they have done is already leading the way to drugs that manipulate oxygen-sensing pathways,” he said.
He added the discovery pointed to a basic principle of human evolution. Murray said particular traits have been noted in people who live at high altitude, like those on the Tibetan plateau, whose bodies have adapted to low oxygen.


Last year, James Allison of the United States and Tasuku Honjo of Japan won the 2018 Nobel Prize for Medicine for their work in immunotherapy, activating the bodys natural defense system to fight tumors.
Mondays announcement kicked off this years Nobel Prizes. The Nobel Physics prize is handed out Tuesday, followed by the chemistry prize on Wednesday. This years double-header Literature Prizes—one each for 2018 and 2019—will be awarded Thursday and the Peace Prize will be announced on Friday.
The 2018 Nobel Literature prize was suspended after a sex abuse scandal rocked the Swedish Academy, the body that awards the literature prizes, so they are awarding two prizes this year.
The economics prize will be awarded next Monday. Officially known as the Bank of Sweden Prize in Economic Sciences in Memory of Alfred Nobel, it wasnt created by Nobel, but by Riksbanken, Swedens central bank, in 1968.
The laureates will receive their awards at elegant ceremonies in Stockholm and Oslo on Dec. 10—the anniversary of Nobels death in 1896.
By Maria Cheng, Christopher Chester and Michael Warren
]]> Long-Lost 2,200-Year-Old Egyptian Temple From Reign of King Ptolemy IV Unearthed https://www.theepochtimes.com/long-lost-2200-year-old-egyptian-temple-from-reign-of-king-ptolemy-iv-unearthed_3108415.html Mon, 07 Oct 2019 14:06:06 +0000 A 2,200-year-old long-lost ancient temple linked to Pharaoh Ptolemy IV has been discovered by archaeologists in Egypt, according to reports.
The temple ruins were accidentally found in early September by a group of construction workers in the village of Kom Shakau in northern Sohag as they carried out some drilling work, according to a Facebook post by Egypts Ministry of Antiquities.
After the drilling works were suspended, archaeologists unearthed the temple ruins inscribed with the name of Ptolemy IV, the fourth pharaoh of Egypts Ptolemaic dynasty who is believed to have ruled between 221 B.C. and 204 B.C.
The temples limestone walls and floors are also engraved with inscriptions of birds and flowers surrounding Egypts god of the Niles annual flooding, Hapi, carrying offerings, reported CNN.
An east-west and north-south wall, as well as a southwestern corner have been unearthed so far.
Dr. Mostafa Waziri, general secretary of Egypts Supreme Council of Antiquities, said in a statement on Oct. 6 he had assigned an archaeological mission to recover as much as possible of the ancient temple which sits on the western bank of the Nile.
According to historians, Ptolemy IV did not have a successful reign, and took more interest in pretending to be an artist and overindulging than running his own kingdom.
Sphinx Statue Found in Egyptian Temple
A well-preserved statue of a sphinx was found by archaeologists in a temple in upper Egypt last year.
Archaeologists working on a project to reduce groundwater at the Kom Ombo temple in Aswan, Egypt, uncovered a well-preserved sphinx statue last September, buried on the temples southeast side, near where other relics have recently been found.
Aswan is about 560 miles south of Cairo, on the banks of the Nile River.
Waziri posted on the Ministry Facebook page that the sphinx was found near where two sandstone reliefs of King Ptolemy V had been uncovered about two months earlier.
Waziri believes that the statue dates to the Ptolemaic period, between 305 B.C. and 30 B.C., based on where it was discovered.
Dr. Abd Al-Moneim Al-Sayeed, general director of the Aswan Antiquities, said in the same post that further studies would be undertaken to learn about the origin of the newly uncovered statue.
Sphinx statues are usually found in or near royal tombs. The classic Egyptian sphinx depicts a lions body with a human head, generally the head of whichever pharaoh ruled at the time. The face on this latest statue is extremely well preserved.
The best known sphinx statue, the Great Sphinx of Giza, has an uncertain history. Scholars assume that the current head represents the pharaoh Khafra.
Epoch Times reporter Chris Jasurek contributed to this report.
]]> New Species of Iron Dragon Pterosaur Found in Australia https://www.theepochtimes.com/new-species-of-iron-dragon-pterosaur-found-in-australia_3107526.html Sun, 06 Oct 2019 16:30:25 +0000 Researchers have announced that prehistoric bones found in Australia belong to a new species of pterosaur so fearsome it has been dubbed the “iron dragon.”
A cattle grazier found some fossilized remains in the outback of Queensland in 2017, sparking a broader excavation leading to the Oct. 3 announcement in Scientific Reports that the bones belong to a previously unknown species of pterosaur—a type of flying reptile.


Paleontologists have given this apex predator the Latin name ferrodraco lentoni, or Lentons Iron Dragon, in honor of former Winton mayor Graham “Butch” Lenton, Australias ABC reported.
Adele Pentland of Swinburne University, lead author of the study, told the Sydney Morning Herald where the “iron” came from in reference to the given name of this fearsome predator.
“Pterosaur bones are primarily hollow and thats one reason why theyre so rare in the fossil record,” Pentland explained. “In this case it seems the carcass got covered with sediment very quickly and then iron-rich fluids which have permeated the bones and left behind this really tough rock which filled any voids in there and made them nice and strong.”


Sometimes colloquially referred to as a “winged dinosaur,” this species of pterosaur is believed to have lived around 90 million years ago.
“It would have been a sight to see,” Pentland said, via The Guardian.
“It had a wingspan of four meters,” Pentland added, “which is pretty big compared to our modern-day birds.”
The Iron Dragon remains—which include parts of the skull, five vertebrae, and wing elements—comprise the most complete pterosaur specimen found in Australia to date.
“Even though we didnt find the entire skull, we found most of the skull and we also found 40 teeth and two fragments at the site,” Pentland told The Guardian. “To see it walking around on the ground it would have walked on four legs and looked really different to any kind of animal we have today.”
“Its kind of scary when you think their heads are disproportionately large, it would have had a skull maybe 60 cm.”


Similarities between the ferrodraco and pterosaur species in England have led scientists to infer these aerial predators could fly across oceans, according to Science Alert.
Some dental characteristics led researchers to conclude the ferrodraco pterosaur is a new species.
“The presence of premaxillary and mandibular crests, and spike-shaped teeth with subcircular bases, enable Ferrodraco to be referred to Anhangueria,” the study notes. “Ferrodraco can be distinguished from all other anhanguerian pterosaurs based on two dental characters: the first premaxillary and mandibular tooth pairs are small; and the fourth–seventh tooth pairs are smaller than the third and eighth ones.”
]]> NASA Engineer Used to Struggle With Math As a Student–Now Shes Working on a Lunar Mission https://www.theepochtimes.com/nasa-engineer-used-to-struggle-with-math-as-a-student-now-shes-working-on-a-lunar-mission_3097100.html Sat, 28 Sep 2019 23:04:23 +0000 For Josephine Santiago-Bond, the route to becoming the head of the Advanced Engineering Development Branch at NASA wasnt always an easy one. While this Filipina-American engineer played a big role in a successful lunar exploration mission in 2013, she had to struggle with the same academic challenges as many students all over the world, particularly with mathematics.
But this child of professors has always been guided by a sense of curiosity and willingness to work hard, which have taken her humble beginnings to a key post at NASA.


Appropriately enough, Santiago-Bonds unique background stems from the pursuit for higher education, something that runs in the family. Her Filipino parents were working on their PhDs in the United States when she was born, making her an American citizen by birth.
They returned to the Philippines after completing their studies, and Santiago-Bond grew up in a household where science was everywhere you looked. “I have experienced first-hand how an impressionable child can grow to love science and engineering by simply being exposed to it,” she told Good News Filipinas.
In elementary school, Santiago-Bond got to experiment with chemistry PH indicators her mom had brought home, as she recalled in a NASA profile. “I loved the color combinations that I got from playing with that kit.
“That created a very vivid memory that really influenced me to get into science,” she said.
“My extraordinary is in creating a progressively positive environment for my group of engineers to grow constantly and continue to succeed in research and technology development.” – Josephine Santiago-Bond https://t.co/wm7vdmAXAf pic.twitter.com/kzSRWIga1c
— NASA People (@NASApeople) June 7, 2018
At the age of 12, she left home to attend the Philippine Science High School, which had an intensive program of math and science classes that would prepare her for her engineering career.
Despite this background, Santiago-Bond had difficulties with the daunting courses she would encounter in a five-year program in electronics and communications engineering at the University of the Philippines.
Just as her courses became more interesting, math got “exponentially more difficult,” she told Spot. “I had to crawl my way through some of the courses, but I wasnt going to give up on it because of a few bad grades.”


Working through those tough classes gave her the strength and resolve that would come in handy in her NASA career. “I practiced solving math and engineering problems until I was either confident enough to take the test or ran out of review time,” she told Spot. “There were lots of sleepless nights, but strong friendships were formed, and my persistence eventually paid off.”
When her family relocated to South Dakota, Santiago-Bond went for a Masters degree in electrical engineering at South Dakota State University. Though she had never been especially oriented toward aeronautics, the Columbia space shuttle disaster in 2003 caught her attention.
As she told Asian Journal, “If any good can come out of a disaster like that, I can say that was the point at which I truly started learning and getting interested about NASA and space in general.”


Her university happened to have a summer internship program at the Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Florida, and in the summer of 2004, she went for the first time to the home of the Shuttle program. She loved the work and the warm weather and tropical feel that reminded her of the Philippines.
“What was supposed to be a one-time summer job quickly became permanent because when I came here I fell in love,” as she explains in her NASA profile. Her curiosity continues to drive her as she has worked on lunar exploration projects and recruiting new, diverse talent into the agency.
“Its very rare to find an organization that carries a mission to drive and advance in science and technology, aeronautics and space exploration with just the very simple desire to enhance knowledge all for the benefit of mankind,” she explained to Asian Journal.
Her advice, especially for people whose background is underrepresented in STEM, is to persevere and be fearless. For other women, “I would say to them, dont be afraid of being the only woman in the class … or the only woman in the meeting […]
“A second woman will come along and they would have done her a favor by being the first.”
[youtube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PBpwJSkO3Jc?wmode=transparent&wmode=opaque&w=671&h=377] ]]> Leaders of France, Germany, Australia Rebuke Greta Thunberg https://www.theepochtimes.com/leaders-of-france-germany-and-australia-rebuke-greta-thunberg_3097308.html Thu, 26 Sep 2019 13:25:38 +0000 Leaders of France, Germany, and Australia criticized teenage climate activist Greta Thunberg after she accused them on the world stage of not taking enough action to avert what she calls a “mass extinction.”
French President Emmanuel Macron and German Chancellor Angela Merkel distanced themselves from Thunberg over her speech to the United Nations and a legal complaint Thunberg filed that accuses France and Germany, among other nations, of a lack of action on climate change. Australian Prime Minister Scott Morrison faulted Thunberg for subjecting Australian children to “needless anxiety.”
“Theyve got enough things to be anxious about,” Morrison said of his own daughters. “Weve got to let kids be kids. We cant have them growing up as mushrooms, but weve got to get a bit of context into this.”
Thunberg, 16, has become the face of the global alarmist environmental movement. In her speech to the U.N., she accused world leaders of destroying her “dreams” and her “childhood” with “empty words.”
“People are dying. Entire ecosystems are collapsing. We are in the beginning of a mass extinction, and all you can talk about is money and fairytales of eternal economic growth. How dare you!” Thunberg said.
Thunberg and 15 other child climate activists filed a formal complaint with the U.N. Committee on the Rights of the Child that accuses Argentina, Germany, France, Brazil, and Turkey of violating childrens rights by taking insufficient action to address global warming. The childrens complaint didnt include China and India, the worlds biggest polluters.
Macron, who had previously sided with Thunbergs movement, criticized the youth for taking a radical and antagonistic position.
“All the movements among our youth, or the less young, are useful,” Macron told French broadcaster Europe 1. “But now they must concentrate on the people who are further away, those who are trying to block [sustainable initiatives]. These radical positions will naturally antagonize our societies.”
French Ecology Minister Brune Poirson also criticized Thunberg for creating divisions that may prove irreparable.
“I do not believe that we can mobilize the population with despair, with almost hatred, setting people against one another,” Poirson told Radio France. “Its important, she mobilizes. But what are the solutions she puts on the table? I do not know.”
Merkel, who has said that Thunbergs movement “drove” Germany to take environmental action, took a subtler approach to criticize the teenage climate activist.
“I would like to take the opportunity to strongly contradict her in one matter,” Merkel said, according to The Times of London. “She did not adequately address the way technology and innovation, especially in the energy sector but also in energy conservation, raise possibilities for reaching our goals.”
Macron, Merkel, and Morrison arent the first to criticize climate alarmists. The chief of the World Meteorological Organization, Petteri Taalas, told a Finnish magazine in early September that climate extremists and “doomsters” are attacking mainstream scientists in a bid to shift them toward a radical view of climate change.
“While climate skepticism has become less of an issue, we are being challenged from the other side. Climate experts have been attacked by these people and they claim that we should be much more radical. They are doomsters and extremists. They make threats,” Taalas told Talouselama magazine on Sept. 6.
Taalas said climate extremists are selectively picking out facts from the reports by the UNs Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC).
“The IPCC reports have been read in a similar way to the Bible: you try to find certain pieces or sections from which you try to justify your extreme views. This resembles religious extremism.”
According to Benny Peiser, director of the Global Warming Policy Foundation in London, “Europes political leaders are increasingly concerned about losing their climate agenda to eco-fanatics and extremists.”
Peiser wrote in an email to The Epoch Times: “Gretas apocalyptic mass movement is turning millions of young French, German, and European children and teenagers against their own governments, their institutions, and their countries, turning them into a resentful, angry mob.
“Officials and politicians are beginning to speak out because they fear they may lose control over this increasingly dangerous tiger they thought they could ride forever.”
]]> Second Interstellar Object in History Found in Solar System https://www.theepochtimes.com/second-interstellar-object-in-history-found-in-solar-system_3094788.html Wed, 25 Sep 2019 17:00:48 +0000 An amateur astronomer has found an interstellar object in the solar system, only the second such discovery ever made in history.
The object, named 2I/Borisov was discovered by amateur astronomer Gennady Borisov from MARGO observatory, Crimea, on Aug. 30, according to a statement released by the International Astronomers Union (IAU) on Sept. 24.
The 2I in the name 2I/Borisov refers to its status as the second interstellar object ever discovered. Astronomer Borisov used a self-built 0.65-meter telescope for the discovery. The new object has a condensed coma, or the “fuzzy” part visible through a telescope, and recently a tail has been discovered.
#IAUnews New object from #interstellar space has been found within the Solar System. The object has been given the name #2I/Borisov by the IAU.https://t.co/tki3toW30p
Credit: Gemini Observatory/NSF/AURA pic.twitter.com/zmQ3VOVdf9— Astro Union (@IAU_org) September 24, 2019
“Astronomers are turning their telescopes toward the visitor, which offers a tantalizing glimpse beyond our Solar System and raises some puzzling questions,” said IAU in a statement.
The discovery of 2I/Borisov comes just two years after the discovery of the first interstellar object, 1I/Oumuamua.
“This new finding suggests that such objects may be sufficiently numerous to provide a new way of investigating processes in planetary systems beyond our own,” said IAU.
2I/Borisov is expected to be the brightest in the southern sky in Dec. and Jan.
“2I/Borisov will make its closest approach to the Sun (reach its perihelion) on Dec. 7, 2019, when it will be 2 astronomical units (AU) from the Sun and also 2 AU from Earth,” explained IAU.
Astronomers are excited as the object is going to be observable continuously for many months and longer than the period for which 1I/Oumuamua was visible. They are optimistic about studying it in great detail.
El @GTCtelescope obtiene un espectro del primer cometa interestelar C/2019-Q4 (Borisov) que muestra que el objeto tiene una composición similar a los cometas del Sistema Solar. Más información: https://t.co/4B0sJCmNAO pic.twitter.com/lGyn9p9M0q
— IAC Astrofísica (@IAC_Astrofisica) September 14, 2019
“One of the largest telescopes in the world, the 10.4-meter Gran Telescopio Canarias in the Canary Islands, has already obtained a spectrum of 2I/Borisov and has found it to resemble those of typical cometary nuclei,” said IAU.
The Gran Telescopio Canarias also confirmed the same in a press release. It said that it obtained the first visible spectrum of the interstellar object and a study of the surface composition of 2I/Borisov reveals that it is “not unlike that found in Solar System comets.”
“The spectrum of this object is similar to those of Solar System comets and this indicates that their composition must be similar,” said Gran Telescopio Canarias.
The International Astronomers Union said the presence of 2I/Borisov raises many questions. The scientists would like to know why interstellar objects have not been found before, and at what expected rate they appear in the inner solar system.
“Large telescopic surveys capable of scanning large fractions of the sky on a regular basis may help to answer these questions and more in the near future,” said the IAU.
The Gran Telescopio Canarias said the results of this research “clearly show that comets in other planetary systems can be similar to those of the Solar System.”
]]> Chinas Rivers Are the Major Source of Plastic Entering the Oceans https://www.theepochtimes.com/chinas-rivers-are-the-major-source-of-plastic-entering-the-oceans_3091941.html Mon, 23 Sep 2019 16:55:05 +0000 With 91 percent of the 8.8 million tons of plastic added to oceans each year originating in rivers, the Yangtze and five other Chinese rivers are the dominant polluters.
Pollution of the marine environment with plastic debris is widely recognized as an increasing ecological concern because of the chemical persistence of plastics and their fragmentation into “microplastics,” which can be ingested by small organisms, such as zooplankton, that are eaten by increasingly larger predators in the food chain.
Production of plastics began in 1950 with 2.3 million tons, and has grown to 448 million tons in 2015. 18 percent of plastics produced that is improperly handled after use is referred to by researchers as “mismanaged plastic waste.” Given global production trends, it is estimated that “mismanaged plastic waste” will triple to 170-292 million tons by 2060.
China currently dominates the plastics industry with about 143 million tons of production, or about 29 percent of the global market share. But China for decades also provided reprocessing services for about 70 percent of global plastic recycling.
Almost two thirds of new plastic produced is used for commercial purposes with an average life expectancy of about ten years. But China produces about half of all plastic packaging materials that have an average life expectancy of only six months.
Since most plastic packaging wrap cannot be profitably recycled, much of Chinas domestic plastic waste and imported plastic were disposed of by non-regulated “fly-by-night recyclers” that “dumped stuff they couldnt recycle, causing pollution on land and in waterways,” according to a National Public Radio investigative report.
Of the 8.8 million tons of plastic waste that flows down the worlds “small first order streams to large rivers that discharge to the sea,” the “top ten” polluting rivers account for 88-95 percent of plastics that flow each year into the worlds oceans.
The six Chinese rivers on the “top ten” list—the Yangtze, Yellow, Hai, Pearl, the Amur that borders Russia, and the headlands of the Mekong River—account for about 3.8 million tons, or almost half of the worlds plastic flow into the oceans. The Yangtze alone accounts for 1.6 million tons of plastic discharged into the oceans.
The Chinese regime began cracking down on plastic pollution beginning in 2017, with the central government moving to ban almost all trash imports by mid-2018. The move ended the 700,000 tons of plastic refuse exported each year by the United States to China.
The Huffington Post reported that the city of Shanghai began enforcing mandatory residential and commercial color-coded sorting for garbage: black bins for “dry,” brown for “wet,” blue for “recyclable” and red for “hazardous.” Sorting waste into these categories became mandatory in the city on July 1.
China only recycles about 20 percent of its waste, compared to about 35 percent in the United States. The nation historically relied on millions of “informal” entrepreneurs that dug through the trash containers for plastics and glass to sell. To increase recycling volume, Shanghais fine for each recycling color infraction is now 200 yuan, or about $28.
]]> Australias Morrison Pledges AU$150 Million to Support NASAs Mission to Mars https://www.theepochtimes.com/australian-pm-pledges-150-million-to-support-nasas-mission-to-mars_3090613.html Sat, 21 Sep 2019 17:44:42 +0000 Australian Prime Minister Scott Morrison announced during a visit to NASA headquarters in Washington an AU$150 million (about $102 million) investment in new technology and business to reinforce the U.S. space agencys ambitions of going to the moon and then Mars.
Morrison said in a statement that the Australian Space Agency will be working to “foster the new ideas and high-technology skilled jobs that will make Australian businesses a partner of choice to fit out NASA missions,” The Guardian reported.
“The governments support means Australian businesses and researchers will have the opportunity to showcase their immense knowledge and capabilities in projects that can support NASAs Moon to Mars mission, such as Project Artemis and the Lunar Gateway,” Morrison said.
“The Australian Space Agency will work closely with NASA to identify how they can best support their missions after the signing of a joint statement of intent on expanding cooperation.”
Trump was asked on Sept. 20 about the cooperation between the United States and Australia to develop the space program.
“Were doing a great program,” Trump said, “And you know, were … going to Mars. Were stopping at the moon. The moon is actually a launching pad. Thats why were stopping at the moon.”
“I said, Hey, weve done the moon. Thats not so exciting. They said, No, sir. Its a launching pad for Mars. So well be doing the moon. But well really be doing Mars. And well be—were making tremendous progress.”
The remarks were similar to what Trump wrote on Twitter earlier this year: “For all of the money we are spending, NASA should NOT be talking about going to the Moon – We did that 50 years ago. They should be focused on the much bigger things we are doing, including Mars (of which the Moon is a part), Defense and Science!” said Trump.
For all of the money we are spending, NASA should NOT be talking about going to the Moon – We did that 50 years ago. They should be focused on the much bigger things we are doing, including Mars (of which the Moon is a part), Defense and Science!
— Donald J. Trump (@realDonaldTrump) June 7, 2019
In October 2017, Trump broached the ambitious idea: “We will return Americans astronauts to the moon, not only to leave behind footprints and flags but to build the foundation we need to send Americans to Mars and beyond.”
Under my Administration, we are restoring @NASA to greatness and we are going back to the Moon, then Mars. I am updating my budget to include an additional $1.6 billion so that we can return to Space in a BIG WAY!
— Donald J. Trump (@realDonaldTrump) May 13, 2019
From NTD News
]]> The US Navy Just Confirmed UFO Videos Are the Real Deal https://www.theepochtimes.com/the-us-navy-just-confirmed-ufo-videos-are-the-real-deal_3088194.html Thu, 19 Sep 2019 23:49:49 +0000 The US Navy has finally acknowledged footage purported to show UFOs hurtling through the air. And while officials said they do not know what the objects are, they are not divulging any hints either.
The objects seen in three clips of declassified military footage are “unidentified aerial phenomena,” Navy spokesperson Joe Gradisher confirmed to CNN.
The clips, released between December 2017 and March 2018 by To The Stars Academy of Arts & Sciences, appear to show fast-moving, oblong objects captured by advanced infrared sensors.
In footage from 2004, sensors locked on a target as it was flying before the object accelerated right out of the left side of the video frame, too quickly for the sensors to relocate it.
Two of the videos, both from 2015, contain audio from US fighter pilots attempting to make sense of what theyre seeing.
“Its a [expletive] drone, bro,” a pilot says to his colleague in the first clip.
“My gosh! Theyre all going against the wind.”
“Look at that thing, dude!”
To The Stars Academy of Arts & Science identified two traits that distinguish the flying object captured on this video from cruise missile or conventional aircraft. First, “there are no obvious wings or tails on the object.” Second, “there was no exhaust plume from the object”. Both would have been visible on imagery captured by the advanced infrared multi-sensor camera used by the military aircraft.
Gradisher said the Navys transparency about unidentified aerial phenomena, or UAP, is largely done to encourage trainees to report “incursions” they spot in the airfield which threaten a pilots safety.
“This is all about frequent incursions into our training ranges by UAPs,” he said. “Those incursions present a safety hazard to the safe flight of our aviators and the security of our operations.”
The public clips capture just a fraction of the frequent incursions Navy training ranges see, he said.
“For many years, our aviators didnt report these incursions because of the stigma attached to previous terminology and theories about what may or may not be in those videos,” he said.
The only way to find out what the UAP is, he said, to encourage trainees to report them when they see them.
This footage was released along with an op-ed about UFO phenomena in the Washington Post penned by former deputy assistant secretary of defense for the intelligence of the Clinton and George W. Bush administrations, Chris Mellon. As cited by FigtherSweep.com, Mellon wrote in his op-ed:
“The videos, along with observations by pilots and radar operators, appear to provide evidence of the existence of aircraft far superior to anything possessed by the United States or its allies. Defense Department officials who analyze the relevant intelligence confirm more than a dozen such incidents off the East Coast alone since 2015.”
Ella Kietlinska contributed to this article.
]]> Teen Scientists Discover Bacteria That Can Turn Plastic Waste Into Valuable Chemicals https://www.theepochtimes.com/teen-scientists-discover-bacteria-that-can-turn-plastic-waste-into-valuable-chemicals_3077779.html Wed, 18 Sep 2019 00:02:13 +0000 It all started the day that two curious high school students who were aspiring scientists visited a waste transfer station in Vancouver, Canada. The then-17-year-olds saw tons of unrecycled and unrecyclable plastics.
Then and there, the pair decided that they were going to use their interest in science to find a way to make a difference. Seven years and numerous prizes and awards later, the pair have their own successful startup: BioCellection.
Their mission is nothing less than to save the world from the consequences of plastic waste.
تم النشر بواسطة BioCellection في الجمعة، ١٢ يونيو ٢٠١٥
When best friends Miranda Wang and Jeanny Yao visited the local waste-processing center, they expected to see a high-tech recycling center that could take care of everything the city was producing. After all, Vancouver aspires to be one the greenest cities in the world.
But the reality was different. “We were just astounded at how much plastic packaging goes into a landfill,” Wang told CNN. The problem is that, left to natural processes, the millions of metric tons of plastic produced each year wont degrade like natural materials would. With more and more piling up every year, a MacArthur Foundation report estimates that by 2050, there might be more plastic than fish in the sea.
Time-lapse: BioCellection's invention at work on unrecyclable plastic bags.
تم النشر بواسطة BioCellection في الجمعة، ٩ مارس ٢٠١٨
The problem is that current technologies for recycling plastic are just scratching the surface, as a 2017 study from the journal Science Advances revealed. According to their global survey, “around 9 percent of [mass-produced plastic] had been recycled, 12 percent was incinerated, and 79 percent was accumulated in landfills or the natural environment.”
Conventional recycling techniques have major drawbacks, as they either require plastics to be clean (and thus use a lot of water to wash them) or use a lot of energy to break them down, which makes the process uneconomical. These techniques use a lot of energy themselves, canceling out their viable benefits.
Photo of the day: 8 plastic bags bubbling away into organic acids.
تم النشر بواسطة BioCellection في الاثنين، ٢٩ يناير ٢٠١٨
Rather than look to existing processes, Wang and Yao turned to their local environment for a solution. Their first major discovery was a bacteria from the local river estuary that had evolved to be able to break the plastics down. Drawing on this find, the students sought a way to scale up what was already happening in the natural world.
Creating a catalyst in the lab that works in a similar way, as Wang explained to CNN, their company Biocellection now has a “70 percent conversion from plastic waste material” to chemicals that can be used to make “building blocks for more complex plastic products: nylon for clothes, shoe soles, even automobile parts.”


Biocellection focuses on things like single-use plastic bags and films, which often go unrecycled. Wang and Yao are working on marketing their process, which they claim is cheaper than making new plastic from petroleum. “The cost reduction could be up to 30–40 percent,” Wang told CNN.
Wang, Yao, and their colleagues at Biocellection have won countless awards for their innovative work, most recently a Rolex Laureate Award in 2019. As for their goals for the future, they are aiming high.
[youtube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FRFcqHIF8AQ?wmode=transparent&wmode=opaque&w=671&h=377]
“My dream is to be able to see that something that is a sad piece of plastic—that would right now go to the ocean or landfill—could be used to make a brand-new Patagonia jacket, or a brand-new pair of running shoes, or could be used in other industrial applications,” Wang told CNN.
While some people might be discouraged after learning so much about the scale of the problem, Wang remains optimistic about what can be done if people put their minds to it. “Theres so much creativity out there, so much knowledge in our world,” she shared with CNN. As for all the big global problems, starting with plastics, Wang adds, “I believe were able to solve all of them if we try.”
]]> 2,100-Year-Old IPhone-Like Belt Buckle Found in Siberia, Reports Say https://www.theepochtimes.com/2100-year-old-iphone-like-belt-buckle-found-in-siberia-reports-say_3081037.html Fri, 13 Sep 2019 18:23:25 +0000 A 2,100-year-old belt buckle has been described as “iPhone-like,” leaving an archaeologist in amazement.
Archeologist Pavel Leus, who discovered the item in Tuva, Russia, said it resembled a modern-day smartphone, reported the Siberian Times. He also named the skeleton found near the item “Natasha.”
Natashas burial with a Xiongnu-era iPhone remains one of the most interesting at this burial site,” he told the news outlet.
View this post on Instagram
A post shared by Pavel Leus (@pavel_fahrner) on Sep 7, 2019 at 12:20am PDT
The archaeological finding is actually a 7-inch by 3.5-inch belt buckle, Leus said, adding that it was decorated with Chinese wuzhu coins, which helped researchers date it.
Such coins were minted nearly 2,200 years ago in China, he noted in the report.
View this post on Instagram
A post shared by Pavel Leus (@pavel_fahrner) on Sep 13, 2019 at 1:34am PDT
View this post on Instagram
A post shared by Pavel Leus (@pavel_fahrner) on Sep 6, 2019 at 8:22am PDT
The finding was first made in 2016 at the Al-Tay necropolis in the Sayan Sea, but it went viral after the Siberian Times published photos of the item and its “iPhone” description.
“Archaeologists identified two burial sites—Terezin and Ala-Tey—dating to the Xiongnu period around 2,000 years ago, according to a study co-authored by Leus and published in 2018 in the journal Asian Archaeology,” Live Science reported.
View this post on Instagram
A post shared by Pavel Leus (@pavel_fahrner) on Aug 27, 2019 at 9:43pm PDT
It noted that, however, there are only a few weeks each year when archaeologists can access these locations, said the Russian Geographical Society (RGS).
The sites are located in a flood zone covered by the Sayan Sea. Floodwaters only recede at the end of May until the first half of June, Live Science noted.
Rectangular bronze buckles like the one above have been found in Siberia, Central Asia, and Mongolia. Many of them have carved animal designs, said a report in 2011 from Germanys University of Bonn.
“This site is a scientific sensation,”Marina Kilunovskaya of the St. Petersburg Institute of Material History Culture told GlobalNews.
In the vicinity, two partly mummified skeletons were discovered. One was draped in silks and another was buried with a wooden spindle in a sewing bag.
“We are incredibly lucky to have found these burials of rich nomads that were not disturbed by grave robbers,” Kilunovskaya was quoted as saying.
]]> Newfound Comet Likely an Interstellar Visitor, Scientists Say https://www.theepochtimes.com/newfound-comet-likely-an-interstellar-visitor-scientists-say_3080556.html Fri, 13 Sep 2019 09:02:55 +0000 A newly discovered comet hurtling toward the orbit of Mars has scientists scurrying to confirm whether it came from outside the solar system, a likely prospect that would make it the second such interstellar object observed in our planetary neighborhood.
The trajectory of the comet, first detected by Crimean astronomer Gennady Borisov, follows a highly curved path barreling in the suns direction at unusually high speeds, evidence that it originated beyond the solar system.
“On our team, weve been scrambling here at the University of Hawaii to get observations to make position measurements,” said Karen Meech, an astronomer at the university whose team concluded that the objects size and tail of gas classify it as a comet.
“Every time a new comet is discovered, everybody starts to try and get data so that you can get the orbit,” Meech told Reuters, adding that her researchers “all are 100 percent convinced that this really, truly is interstellar.”
The comet, an apparent amalgam of ice and dust, is expected to make its closest approach to the sun on Dec. 8, putting it 190 million miles (300 million km) from Earth, on a route believed unique to such objects of interstellar origin.
Once confirmed interstellar, the comet—dubbed C/2019 Q4 by astronomers—would become only the second such body ever observed by scientists.
The first was a cigar-shaped comet dubbed Oumuamua—a name of Hawaiian origin meaning a messenger from afar arriving first—that sailed into our planetary neighborhood in 2017, prompting initial speculation that it may have been an alien spacecraft. Astronomers soon reached a consensus that it was not.


Unlike Oumuamua, which visited the solar system for only a week, the newfound comet will linger near Mars orbit for almost a year, giving scientists ample time to characterize its chemical signatures and seek further clues about its origin.
“The high velocity indicates not only that the object likely originated from outside our solar system, but also that it will leave and head back to interstellar space,” said Davide Farnocchia, an astronomer at NASAs Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California.
Oumuamua
By Joey Roulette
]]> Water Found in Atmosphere of Planet Beyond Our Solar System https://www.theepochtimes.com/water-found-in-atmosphere-of-planet-beyond-our-solar-system_3078858.html Thu, 12 Sep 2019 03:48:32 +0000 LONDON—Scientists for the first time have detected water in the atmosphere of an Earth-like planet orbiting a distant star, evidence that a key ingredient for life exists beyond our solar system, according to a study published on Sept. 11.
Water vapor was found in the atmosphere of K2-18b, one of hundreds of “super-Earths”—worlds ranging in size between Earth and Neptune – documented in a growing new field of astronomy devoted to the exploration of so-called exoplanets elsewhere in the Milky Way galaxy.
More than 4,000 exoplanets of all types and sizes have been detected overall.
The latest discovery was reported in research by a team of scientists at University College London (UCL) published in the peer-reviewed journal Nature Astronomy.
“We found water,” UCL astrophysicist Ingo Waldmann told Reuters of the breakthrough, revealed from observations made with the Hubble Space Telescope, which analyzed starlight filtered through K2-18bs atmosphere.


More precisely, it marks the first time scientists have found water in the atmosphere around a super-Earth—as opposed to a gas giant—orbiting a star within its “habitable zone,” just the right distance for liquid water to potentially exist on the surface.
Angelos Tsiaras, an astronomer at UCL, said the team is focusing its attention on identifying exoplanets with conditions similar to those on Earth.
“But of course this is not in order to find a place where we could go. This is still science fiction,” Tsiaras said, noting that K2-18b orbits a dwarf star in the constellation Leo that lies 100 light years from Earth.
While light from the sun takes several minutes to reach Earth, light from K2-18bs star takes a century to reach our planet, “so for us to travel there is impossible,” he said.
“Given its so far away we dont really have any other choice but stay on our own Earth, so its important to make Earth great again rather than looking for an alternative to go to,” Tsiaras said.
Aside from the tremendous distance separating Earth from K2-18b, the exoplanet is likely exposed to far more radiation than Earth, diminishing the prospects for life evolving there.
However, the discovery brings astronomers closer to answering the fundamental question of how unique Earth is in the universe, the scientists said.
By Barbara Goldberg
]]> Asteroid That Killed the Dinosaurs Caused a Tsunami That Dumped Tons of Rocks, Say Researchers https://www.theepochtimes.com/asteroid-that-killed-the-dinosaurs-caused-a-tsunami-that-dumped-tons-of-rocks-say-researchers_3077442.html Wed, 11 Sep 2019 10:17:48 +0000 Researchers have revealed new evidence suggesting what happened on the day the dinosaurs went extinct.
A new study led by the University of Texas Institute for Geophysics (UTIG) at Austin found the asteroid that killed the dinosaurs 66 million years ago created massive tidal waves that shifted hundreds of feet of rocks into the impact crater it left behind.
UTIG Research Professor Sean Gulick estimates it only took 24 hours before the crater was filled with about 425 feet of material from the nearby Gulf of Mexico, making it the highest ever amount of rock moved in geological history.
“Its an expanded record of events that we were able to recover from within ground zero,” Gulick said in a statement on Sept. 9. “It tells us about impact processes from an eyewitness location.”
“A New Timeline of the Day the Dinosaurs Began to Die Out” – NYTs take on @SeanGulick, @glchristeson and cos new study of the Chicxulub rocks https://t.co/2Hjz5xi6ee
— UTIG (@UTGeophysics) September 11, 2019
In 2016, his International Ocean Discovery Program scientific drilling mission retrieved bits of charcoal, sand, jumbles of rock, and a chemical biomarker associated with soil fungi off the shore of the Yucatan Peninsula, 770 miles east of Mexico City. This suggests the charred landscape was pulled into the crater with receding waters of tsunamis.
There was strangely no sulfur in the many melted and broken specimens of sandstone, limestone, and granite, even though the area usually has a high concentration of rocks containing sulfur. Gulicks team of more than 24 scientists suggests the impact vaporized these rocks and released at least 325 billion metric tons of sulfate aerosols into the atmosphere that reflected sunlight away from the surface, causing cooling on a global scale.
New research led by @SeanGulick of @UTGeophysics tracks the first 24-hours of the extinction of the dinosaurs and finds evidence for what did them in on the global level: https://t.co/0seTCdzb9w pic.twitter.com/JPSIC5LWul
— Geosciences @UT (@txgeosciences) September 9, 2019
In comparison sulfur released into the atmosphere during the 1883 eruption of the Krakatoa Volcano in Indonesia was only a quarter of the size and still cooled the Earths climate by an average of 2.2 degrees Fahrenheit for five years.
The team estimates the asteroid delivered the equivalent of 10 billion atomic bombs that killed 75 percent of life on Earth. The resulting wildfires, tsunamis that reached as far inland as Illinois, and concentration of sulfur released into the atmosphere worldwide was so great it blocked the sun and eventually caused a global Ice Age.
“We fried them and then we froze them,” Gulick said. “Not all the dinosaurs died that day but many dinosaurs did.”
He revealed the mass extinction of dinosaurs was more of a product of global cooling rather than simply the asteroid impact.
“The real killer has got to be atmospheric,” Gulick said. “The only way you get a global mass extinction like this is an atmospheric effect.”
The research team received funding from the National Science Foundation and other support organizations.
UTIGs Sean Gulick is on @KUT at 10 a.m. CDT this morning about upcoming research project to core into crater of dinosaur-killing asteroid.
— UTIG (@UTGeophysics) April 7, 2015
]]>
Its Possible Alien Civilizations Have Explored the Milky Way, Visited Earth Millions of Years Ago: Study https://www.theepochtimes.com/its-possible-alien-civilizations-have-explored-the-milky-way-visited-earth-millions-of-years-ago-study_3075841.html Tue, 10 Sep 2019 15:09:34 +0000 Aliens or non-human civilized life within our own Milky Way could have already visited Earth but we just arent aware of it, a new study says.
The study, published Aug. 20 in The Astronomical Journal, examines the Fermi Paradox and suggests that its possible that alien civilizations have visited Earth but that it was so long ago, we werent around to see it. The study set out to examine the Fermi Paradox, which questions why we havent been able to detect signs of alien life.
Referring to the possibility of travel between stars by extraterrestrial life, if it exists, physicist Enrico Fermi once famously asked: “Where is everybody?”
The study says that interstellar alien civilizations could simply be taking a strategic and timed approach to traveling the galaxy by utilizing the movement of star systems to migrate.
“If you dont account for motion of stars when you try to solve this problem, youre basically left with one of two solutions,” Jonathan Carroll-Nellenback, a computational scientist and the studys lead author, told Business Insider. “Either nobody leaves their planet, or we are in fact the only technological civilization in the galaxy.”
Carroll-Nellenback said his findings challenged a paper by astrophysicist Michael Hart who argued in 1975 that it is unlikely other civilized lifeforms had not already been discovered in the 13.6 billion-year-old galaxy. Carroll-Nellenback said that Hart hadnt taken into account movement the of our galaxy in his research that could influence the timing of interstellar travel.
While planets orbit stars, the galactic center is also orbited by star systems. It takes 230 million years for our solar system to orbit the Milky Way.
Taking into account the fact that solar systems orbit at various speeds, the study says its possible that alien lifeforms could be waiting for habitable zones to move closer to them. This could mean that extraterrestrials may have visited earth millions of years before humans evolved, or they may not have reached Earth yet, according to the paper.
“Habitable worlds are so rare that you have to wait longer than any civilisation is expected to last before another one comes in range,” Carroll-Nellenback told Business Insider.
He added that discouraging research on the topic so far doesnt mean alien life isnt out there.
“It doesnt mean that were alone,” he said. “It just means that habitable planets are probably rare and hard to get to.”
The paper concluded that to rule out the possibility of any life on all of the galaxys estimated habitable planets would be like failing to find dolphins in a pool-sized patch of the ocean and then claiming that there are no dolphins.
Alien Life May Exist on Planet 30 Trillion Miles From Earth
Researchers say that alien life could possibly exist on a planet 30 trillion miles from Earth.
Barnard B, the planet that orbits around Barnards Star, could have the potential for life if water exists there, according to study published by astrophysicists at Villanova University in January. The star is located some six light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Ophiuchus and is the fourth-nearest known star to the Sun.
An ocean could provide the possibility for the existence of primitive life due to geothermal heating.
“Geothermal heating could support life zones under its surface, akin to subsurface lakes found in Antarctica,” said one of the authors, Edward Guinan, in a statement.
According to the paper, the temperature on Barnard B is similar to Europa, Jupiters moon—roughly 238 degrees Fahrenheit below zero.

But if there is water on the planet, geothermal heating could provide conditions for life in an otherwise inhospitable environment, the researchers say.
“We note that the surface temperature on Jupiters icy moon Europa is similar to Barnard b but, because of tidal heating, Europa probably has liquid oceans under its icy surface,” Guinan said in the statement.
Epoch Times reporter Jack Phillips contributed to this report.
]]> Physics Professor Awarded $800,000 Compensation After University Fires Him Unlawfully for Views on Great Barrier Reef https://www.theepochtimes.com/climate-skeptic-professor-awarded-800000-compensation-after-university-fires-him-unlawfully_3071558.html Fri, 06 Sep 2019 19:41:38 +0000 A court has awarded Australian academic Dr. Peter Ridd over A$1.2 million ($800,000) in damages after finding the physics professor was unlawfully fired after taking a skeptical stance on some of the impacts of climate change.
In a judgment (pdf) issued on Sept. 6, the Federal Circuit Court of Australia ruled to award Ridd “the sum of 125,000 AUD [$82,000] by way of pecuniary penalty” plus “1,094,214.47 AUD [$750,397.39] as compensation for loss” that the former James Cook University employee suffered at the hands of the educational institution.
Ridd was reported by WAToday as having sparked the ire of the university for challenging his colleagues research on how the Great Barrier Reef has been impacted by global warming. Exemplifying his perspective are arguments he made in the publication “Climate Change: The Facts 2017” (pdf) in which he wrote that coral is the “least endangered of any ecosystem to future climate change.”
Questions About Questionable Science
“There is perhaps no ecosystem on Earth better able to cope with rising temperatures than the Great Barrier Reef,” Ridd wrote in the publication. “Irrespective of ones views about the role of carbon dioxide (CO2) in warming the climate, it is remarkable that the Great Barrier Reef has become the ecosystem, more than almost all others, that is used to illustrate and claim environmental disaster from the modest warming we have seen over the course of the last century.”
“I have highlighted just a few examples of questionable science—the list is long,” Ridd continues, adding that in his view, current scientific practices and institutions are unreliable and in need of reform.
“The fundamental problem is that we can no longer rely on the science, or for that matter our major scientific institutions. There are major quality assurance shortcomings in the way we conduct what I will call policy science—that is science used to inform public policy.”
In particular, Ridd argues for the need for rigorous quality assurance with respect to scientific studies that inform policy.
“Policy science concerning the Great Barrier Reef is almost never checked,” he wrote. “Over the next few years, Australian governments will spend more than a billion dollars on the Great Barrier Reef; the costs to industry could far exceed this. Yet the keystone research papers have not been subject to proper scrutiny. Instead, there is a total reliance on the demonstrably inadequate peer-review process.”
He concludes: “There are serious problems with quality assurance in many areas of science, and possibly more so for Great Barrier Reef policy science. Not only are there the normal science distorting factors, such as only being able to get funding when there is a problem to be solved, there is also the problem that many marine scientists are emotionally attached to their subject. The world needs people who care for the environment; many of these scientists have signed up for a career of relative poverty to pursue marine biology. However, given these emotional pressures, together with the lack of a formal quality assurance mechanism, and documented examples of misinterpretation of calcification rates, we can be skeptical of claims that the Great Barrier Reef is in peril.”
Ridd is also on record for taking a skeptical stance on the mainstream climate science consensus more broadly, after former President Barack Obama said in 2008, “few challenges facing America and the world are more urgent than combating climate change. The science is beyond dispute and the facts are clear.” The professor was a signatory to a full-page ad funded by the Cato Institute that disputed Obamas characterization, noting that “the case for alarm regarding climate change is grossly overstated.”
“Surface temperature changes over the past century have been episodic and modest and there has been no net global warming for over a decade now,” the ad reads. “After controlling for population growth and property values, there has been no increase in damages from severe weather-related events. The computer models forecasting rapid temperature change abjectly fail to explain recent climate behavior. Mr. President, your characterization of the scientific facts regarding climate change and the degree of certainty informing the scientific debate is simply incorrect.”
Other notable opinions expressed by Ridd include saying in an interview on The Bolt Report that the climate change debate is unfairly skewed to favor one side, comparing it to a “court case in China,” and saying that those representing the modern green movement “nowadays are less of an environmental movement and more of an extreme left-wing conglomeration devoted primarily to social justice issues.”
No Joke
In its decision, the Federal Circuit Court listed a total of 18 “contraventions” of legal acts that the university had in April been found guilty of, including imposing a gag order on Ridd “to keep the disciplinary process confidential;” trying to prevent him from making jokes about his ordeal by directing him to refrain from “make[ing] any comment or engag[ing] in any conduct that directly or indirectly trivialises, satires or parodies the University taking disciplinary action against [him];” and, finally, firing him.
Judge Salvatore Vasta wrote in the judgment that Ridd would now be seen as “damaged goods” and the university had “poisoned the well” of the professors future employability.
“The fact that JCU has not removed either of their press statements (despite my judgement) is almost tantamount to an attempt to ensure that Professor Ridd does not obtain employment in this field,” Judge Vasta noted.
The judge further suggested the universitys conduct bordered on “paranoia and hysteria fuelled by systemic vindictiveness” and Ridd must have felt he was being persecuted. He found the academics intellectual freedom had been undermined by the “myopic and unjustified actions of his lifelong employer.”
Reacting to the courts determination, Ridd said, “this case was always about academic freedom. It was a fight that should never have started in the first place.” He pointed to his decades-long history of empirical inquiry into the Great Barrier Reef, saying that it is his “genuinely held belief is that there are systemic quality assurance problems at GBR science institutions. I had a right, a duty, to say this. JCU have still not accepted this fundamental right despite the importance of the debate to the North Queensland region.”
The university has three weeks to appeal the ruling. If they do, Ridd said he will continue to press his case.
“My lawyers say it is a landmark case so it is imperative that we continue the fight if necessary,” he said.
WAToday reported that on Friday, the university declared its intent to appeal.
“The university has previously made clear its intention to appeal His Honours decision in this matter. As a litigant it is entitled to do so. The universitys position will be addressed in its appeal,” a spokesman said, according to the report.
]]> Doctor From the Congo Finds Cure for Ebola Virus With Breakthrough New Treatment https://www.theepochtimes.com/doctor-from-the-congo-finds-cure-for-ebola-virus-with-breakthrough-new-treatment_3065471.html Wed, 04 Sep 2019 16:01:06 +0000 This past year, the Democratic Republic of Congo has been battling the second-largest Ebola outbreak in recorded history.
Ebola is a highly contagious virus carried by insects and animals that causes severe bleeding and organ failure in humans, making it incredibly deadly if not treated quickly. In a place where the population is incredibly transient and distrustful of authorities, like the rebellion-torn Congo, the struggles to act quickly against confirmed cases has resulted in fatalities for two out of every three confirmed cases discovered during this current outbreak.
Luckily, a Congolese doctor has been dedicating the last four decades to discovering a cure for the virus—and based on the results from his most recent medical trials, he may very well have succeeded.

Dr. Jean-Jacques Muyembe Tamfum is now 77 years old, but hes been working on Ebola research since the first known outbreak of the disease in 1976.
A pair of drugs that he recently used in test patients, though, officially cured both individuals and allowed them to return home safely. This, Muyembe explained, can help spread the word that not only is Ebola real—cultural distrust of medical workers in the region has left many skeptical that the virus truly exists—but that there is a way to cure it with modern medicine.
2 Ebola patients in Congos Goma treated successfully with new drugs https://t.co/KcKgVSCPge pic.twitter.com/RvEhGivSlI
— CBC World News (@CBCWorldNews) August 13, 2019
The two drugs, named REGN-EB3 and mAb114, were developed by Muyembe using antibodies harvested from blood samples taken from surviving Ebola patients during previous outbreaks. Over the 43 years that Muyembe has been working to combat Ebola outbreaks with the World Health Organization, hes been patiently developing the idea to use the antibodies to block the virus from attacking human cells—and now, it appears that hes found a way to do that.
Moving forward, Muyembe hopes to spread the word that Ebola is no longer incurable. This could lead to earlier detection, which could lead to individuals getting treated faster and slow the speed of the current outbreak. Getting afflicted patients to leave their homes and protect their loved ones will help contain the virus, slowing its progression through the Congolese population and hopefully eradicating this current outbreak once and for all.
Posted by Jean Jacques Muyembe on Monday, March 25, 2013
“Ebola kills quickly and Ebola heals quickly. Thats the message,” said Muyembe, at a press conference in Goma.
“These cases were detected very quickly. The husband was infected, he was at home for 10 days and his wife and son were infected,” said Muyembe. “As soon as the response teams detected these cases, they brought them here to the treatment center. We gave them treatment that is effective and here in a short time both are cured.”


The ultimate goal will still be to vaccinate the population in order to prevent another outbreak from starting. The Ebola virus has an incubation period of anywhere between two and 21 days, and it can be spread from human to human through everything from blood and saliva to semen and breast milk. Infected individuals often spread the disease to their loved ones before they even realize theyve contracted the virus themselves, which makes it even harder to contain.
The way these two experimental drugs work, though, could make for an effective vaccine to help protect the population. After 43 years, Muyembe has managed to succeed in what he set out to do—and innumerable lives may be saved because of it.
]]> Mysterious Wooden Vessel Washes Ashore in Ireland With a Strange Message Inside https://www.theepochtimes.com/mysterious-wooden-vessel-washes-ashore-in-ireland-with-a-strange-message-inside_3060897.html Sat, 31 Aug 2019 22:28:57 +0000 When the coastguard was alerted about a strange vessel that had washed ashore in County Mayo in Ireland, no one could have expected what they were about to find. The unique, handmade wooden contraption had floated all the way across the Atlantic from Canada, and had locals wondering about how it got there.
Unusual items getting washed ashore is a common thing of course. But in the fall of 2016, officials were dumbfounded at the contraption that turned up. It was a wooden houseboat built on polystyrene, about 20 feet long and 10 feet wide, with solar panels on its roof. There was no one aboard.
All things considered, the ship was in remarkably good shape, though it was filled with debris and had seen some wear and tear.
Posted by Ballyglass Coast Guard Unit on Tuesday, May 15, 2018
Inside the houseboat, there was a mysterious handwritten message scrawled on the wall, which the previous owner apparently wrote. It read: “I, Rick Small, donate this structure to a homeless youth to give them a better life that Newfoundlanders choose not to do! No rent, no mortgage, no hydro.”
What puzzled authorities the most was the seeming likelihood that this solar-powered wooden contraption had made its way all the way from Canada.
“To think this apparatus could have come all the way across the Atlantic Ocean,” Michael Hurst, an officer of the Ballyglass Coast Guard Unit, told ABC News, “[is] quite something.”
Mayo / Canadian Houseboat on dry land for the night. Decision as to what happens next rests with Mayo County Council. More on @rtenews pic.twitter.com/OZKVGASvO0
— Pat McGrath (@patmcgrath) November 14, 2016
As the mystery of the boats origin unraveled, it was discovered that the boats builder was Rick Small, a Canadian environmentalist from Thunder Bay, Ontario. Small had only a year prior made headline news in Canada when he rode a solar-powered bike from British Columbia to Newfoundland. That is a distance of 7,000 kilometers (approx. 4,000 miles).
Hurst stated, per ABC, that several residents from Newfoundland contacted County Mayo officials with recollections of having seen Small back in 2015 with the houseboat. One such resident, Timothy Legrow, not only sent a picture of the boat parked at his local docks but also recalled a conversation he had had with the owner. The man had told him that Small was planning to cross the Atlantic with the wooden boat. “He told me his plan was to take the boat and prove that solar power could sail it across the Atlantic,” said Legrow, per an ABC report.
A note found in the vessel says: "I, Rick Small, donate this structure to a homeless youth to give them a better life…" (via BBC News NI)
Posted by BBC News on Monday, November 14, 2016
After being recovered, the boat was taken inland, where it was to stay and wait to be claimed by its owner. But authorities didnt think that was likely to happen. “From the message inside, he likely abandoned that idea and just left the boat on a dock for homeless people,” Hurst told ABC News.
“It probably broke off and somehow made its way across the ocean to here.”
But it still remains a mystery how the boat managed to cross such an enormous distance without a crew and arrive on the Irish shore intact. The vessel had been weatherproofed with tar, and according to one local, was “well made.”
Hurst did reveal plans to repair and turn the contraption into a tourist attraction if its creator never claims it. “If it pans out this way, and if Rick Small doesnt actually require the vessel back, they may use it locally as a tourist attraction and restore it to the best of their ability,” he told Read More – Source
[contf]
[contfnew]

The Epoch Times
[contfnewc]
[contfnewc]



















































 ___________________ https://www.3sat.de/wissen/nano/190913-guertelschnalle-nano-102.html ___________________ #Тува #Ала_Тей #Хунну #сюнну #ТАЭ_ИИМК_РАН #ИИМК_РАН #Саянское_море #экспедициявтуве #археология #Xiongnu #ala_tey #Archaeology #expeditionintuva #archäologie #grabungen #xiongnu_iphone #excavations #ihmc_ras #Tuva #3satnano
___________________ https://www.3sat.de/wissen/nano/190913-guertelschnalle-nano-102.html ___________________ #Тува #Ала_Тей #Хунну #сюнну #ТАЭ_ИИМК_РАН #ИИМК_РАН #Саянское_море #экспедициявтуве #археология #Xiongnu #ala_tey #Archaeology #expeditionintuva #archäologie #grabungen #xiongnu_iphone #excavations #ihmc_ras #Tuva #3satnano


